| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
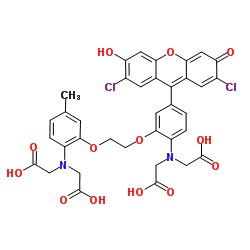 |
Fluo-3
CAS:123632-39-3 |
|
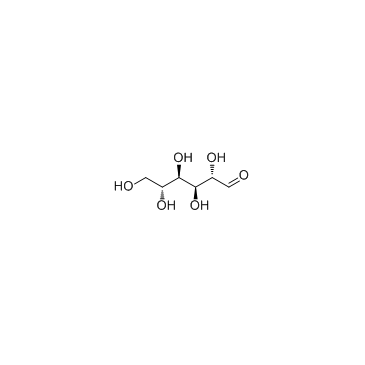 |
D-Mannose
CAS:3458-28-4 |
|
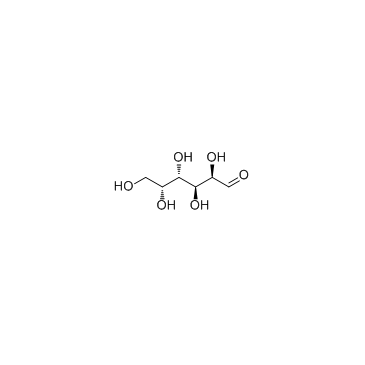 |
D-Galactose
CAS:59-23-4 |
|
 |
BAPTA-AM
CAS:126150-97-8 |
|
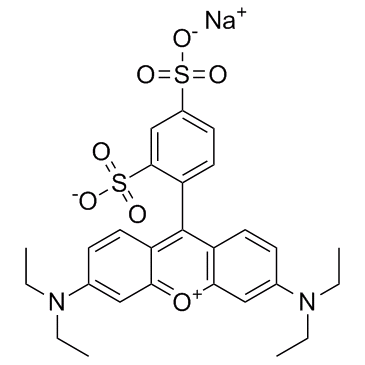 |
Acid Red 52
CAS:3520-42-1 |
|
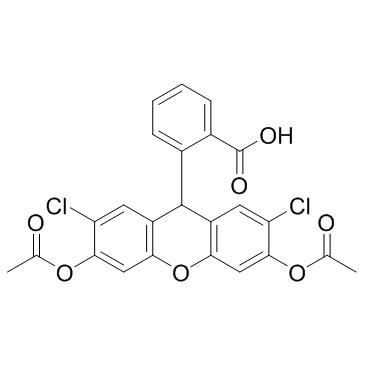 |
H2DCFDA
CAS:4091-99-0 |
|
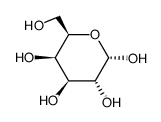 |
galactose
CAS:3646-73-9 |