BAPTA-AM
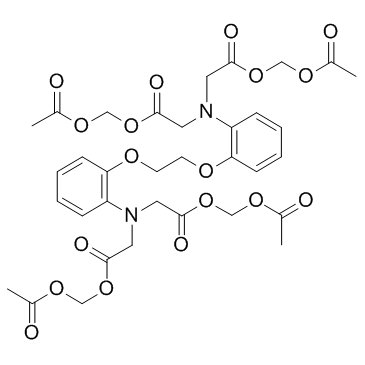
BAPTA-AM structure
|
Common Name | BAPTA-AM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 126150-97-8 | Molecular Weight | 764.684 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 796.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C34H40N2O18 | Melting Point | 86-90°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 435.3±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of BAPTA-AMBAPTA-AM is an intracellular calcium chelator. |
| Name | acetyloxymethyl 2-[N-[2-(acetyloxymethoxy)-2-oxoethyl]-2-[2-[2-[bis[2-(acetyloxymethoxy)-2-oxoethyl]amino]phenoxy]ethoxy]anilino]acetate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | BAPTA-AM is an intracellular calcium chelator. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
calcium chelator[1] |
| In Vitro | The permeable calcium chelator BAPTA/AM is known to prevent free radical-mediated toxicity promote apoptosis in non-neuronal cells and produce a beneficial effect in neuronal cells by protecting neurons from ischemic damage. In addition, it has been suggested that BAPTA/AM induces a late, but not early, increase of intracellular calcium in I-IL-60 neoplastic cells. Mixed cortical cell cultures (DIV 13-16) exposed to 10μM BAPTA/AM for 24- or 48-hr show moderate (45-70%) neuronal injury as evaluated by increased LDH release into the bathing medium after 24-48-hr. Exposure of cortical cultures to 3-10 μM BAPTA/AM for 48-hr evoke dose-dependent neuronal damage[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Neuronal injury is quantitatively estimated by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) released from damaged cells into the bathing medium 24- or 48-hr after the 10 μM BAPTA/AM treatment. The morphological findings are confirmed by staining with neuron-specific enolase (NSE) antibody and tryphan blue[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 796.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 86-90°C |
| Molecular Formula | C34H40N2O18 |
| Molecular Weight | 764.684 |
| Flash Point | 435.3±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 764.227600 |
| PSA | 235.34000 |
| LogP | 2.28 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.551 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Light Sensitive |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Caspase-dependent cell death-associated release of nucleosome and damage-associated molecular patterns.
Cell Death Dis. 5 , e1494, (2014) Apoptosis, which is anti-inflammatory, and necrosis, which is pro-inflammatory, represent the extremes of the cell death spectrum. Cell death is complex and both apoptosis and necrosis can be observed... |
|
|
Kinetics of human sperm acrosomal exocytosis.
Mol. Hum. Reprod. 21(3) , 244-54, (2015) The acrosome reaction is a unique event in the lifespan of sperm characterized by the exocytosis of the acrosomal content and the release of hybrid vesicles formed by patches of the outer acrosomal me... |
|
|
Mechanosensitive store-operated calcium entry regulates the formation of cell polarity.
J. Cell Physiol. 230 , 2086-97, (2015) Ca(2+) -mediated formation of cell polarity is essential for directional migration which plays an important role in physiological and pathological processes in organisms. To examine the critical role ... |
| tetraacetoxymethyl ester |
| Tetrakis(acetoxymethyl) 1,2-Bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetate |
| 1,2-Bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic Acid Tetrakis(acetoxymethyl) Ester |
| MFCD00036696 |
| Tetrakis(acetoxymethyl) 2,2',2'',2'''-[1,2-ethanediylbis(oxy-2,1-phenylenenitrilo)]tetraacetate |
| Tetrakis(acetoxymethyl) 2,2',2'',2'''-[ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy-2,1-phenylenenitrilo)]tetraacetate |
| BAPTA-acetoxymethylester |
| BAPTA-AM |