| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
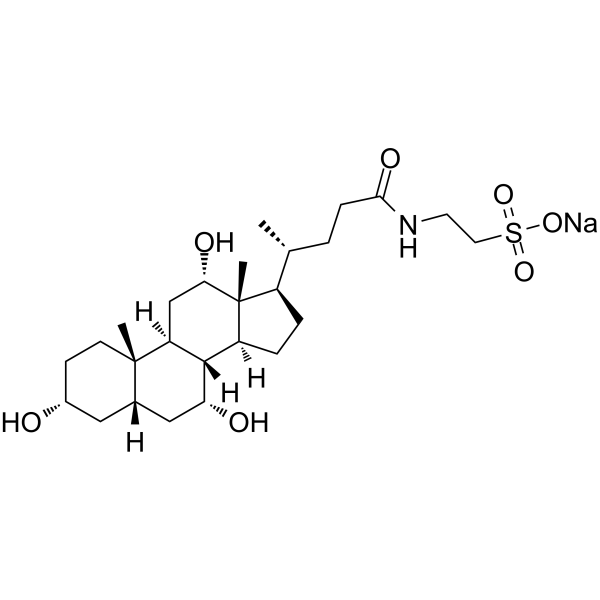 |
Sodium taurocholate
CAS:145-42-6 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
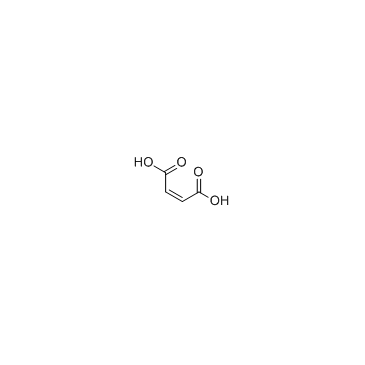 |
Maleic acid
CAS:110-16-7 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
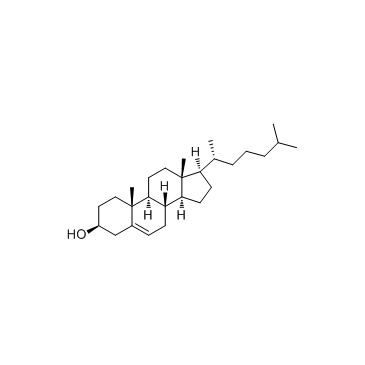 |
cholesterol
CAS:57-88-5 |