| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Potassium bromide
CAS:7758-02-3 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
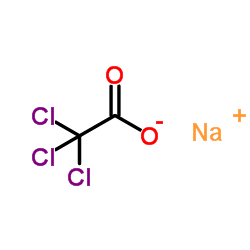 |
Sodium TCA
CAS:650-51-1 |
|
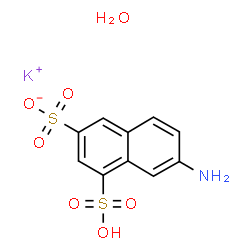 |
1,3-Naphthalenedisulfonic acid, 7-amino-, monopotassium salt, monohydrate
CAS:303137-06-6 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
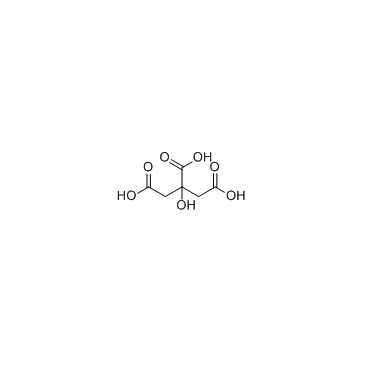 |
Citric Acid
CAS:77-92-9 |
|
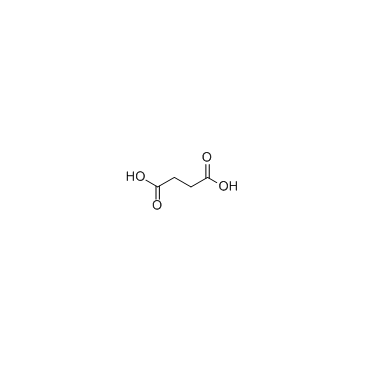 |
Succinic acid
CAS:110-15-6 |