| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Ketoconazole
CAS:65277-42-1 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
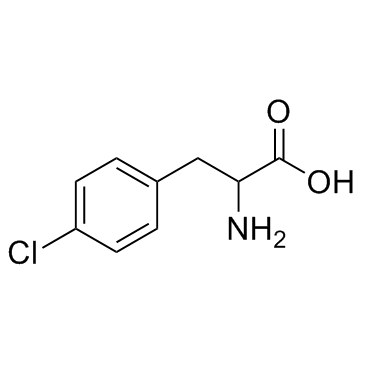 |
DL-4-Chlorophenylalanine
CAS:7424-00-2 |
|
 |
Clotrimazole
CAS:23593-75-1 |
|
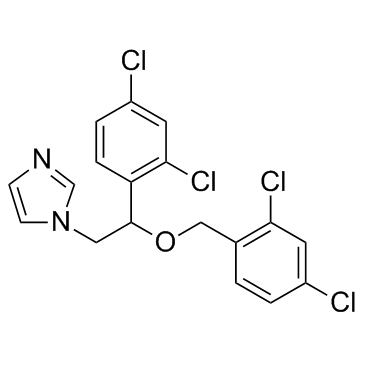 |
Miconazole
CAS:22916-47-8 |
|
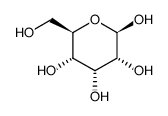 |
Beta-D-allose
CAS:7283-09-2 |