| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
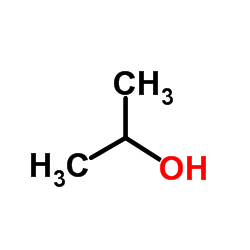 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
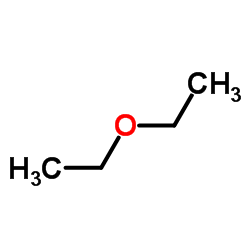 |
Diethyl ether
CAS:60-29-7 |
|
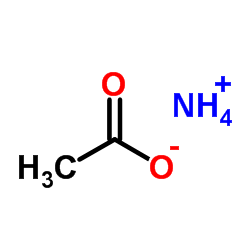 |
Ammonium acetate
CAS:631-61-8 |
|
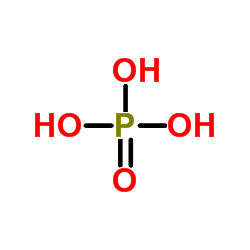 |
Phosphoric acid
CAS:7664-38-2 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |