| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
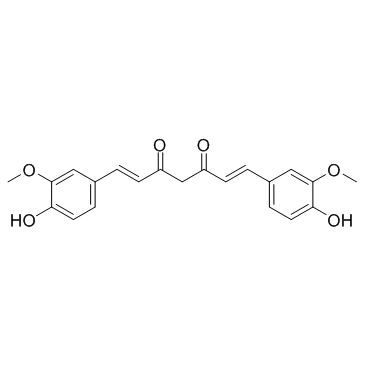 |
Curcumin
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
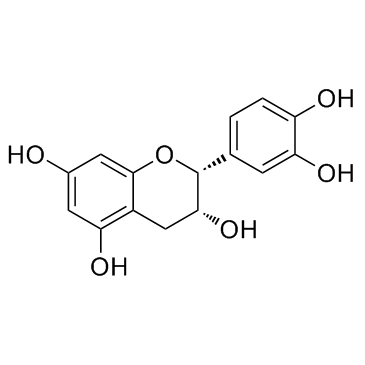 |
Epicatechin
CAS:490-46-0 |
|
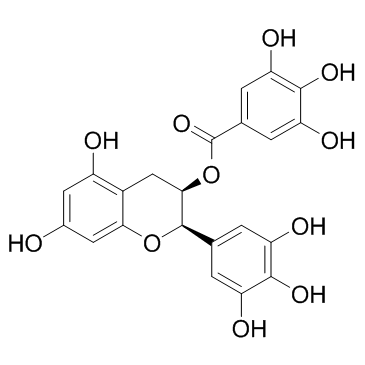 |
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate
CAS:989-51-5 |
|
 |
Lovastatin
CAS:75330-75-5 |
|
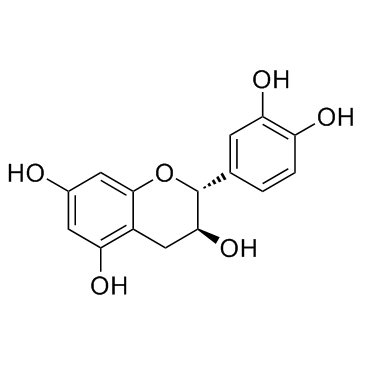 |
Catechin
CAS:154-23-4 |