| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
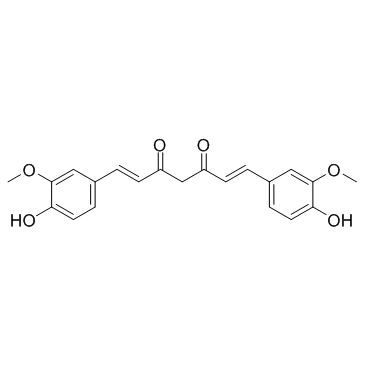 |
Curcumin
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
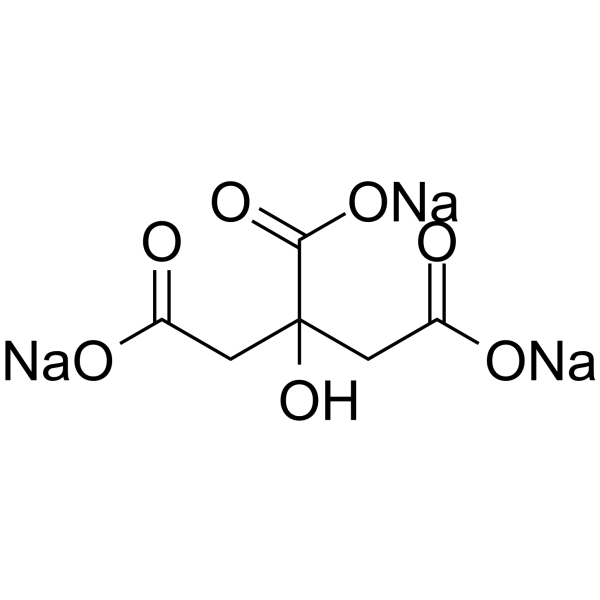 |
Sodium citrate
CAS:68-04-2 |
|
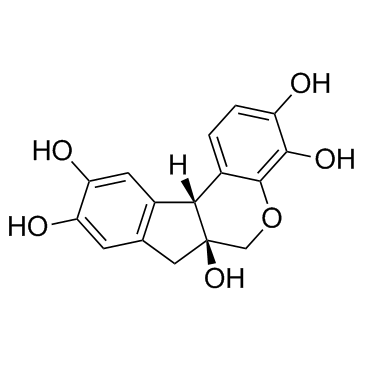 |
Hematoxylin
CAS:517-28-2 |
|
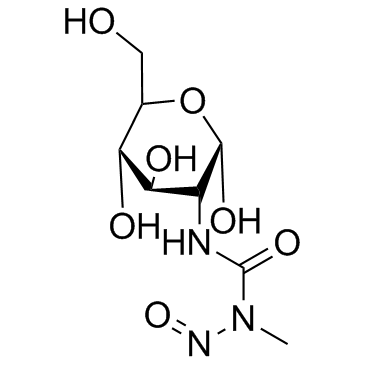 |
Streptozotocin
CAS:18883-66-4 |
|
 |
4,4′-bis(N-carbazolyl)biphenyl
CAS:58328-31-7 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
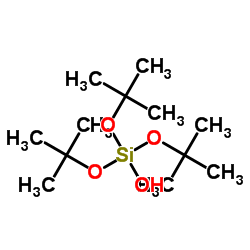 |
Tris(2-methyl-2-propanyl) hydrogen orthosilicate
CAS:18166-43-3 |
|
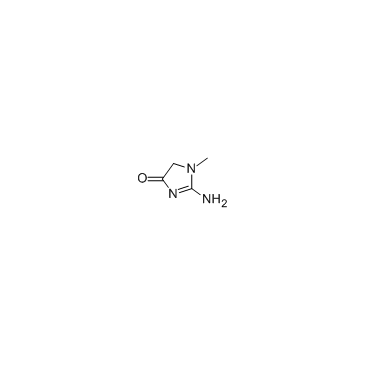 |
Creatinine
CAS:60-27-5 |