| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
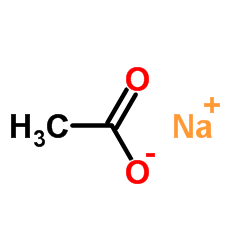 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
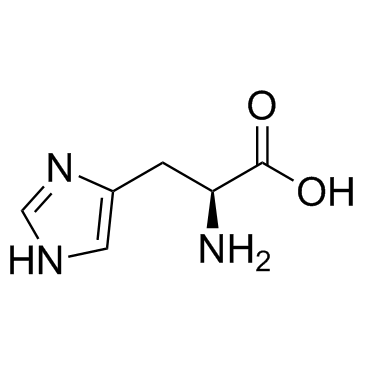 |
L-Histidine
CAS:71-00-1 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
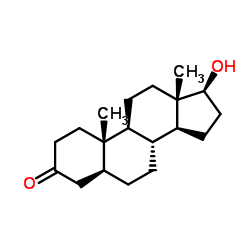 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
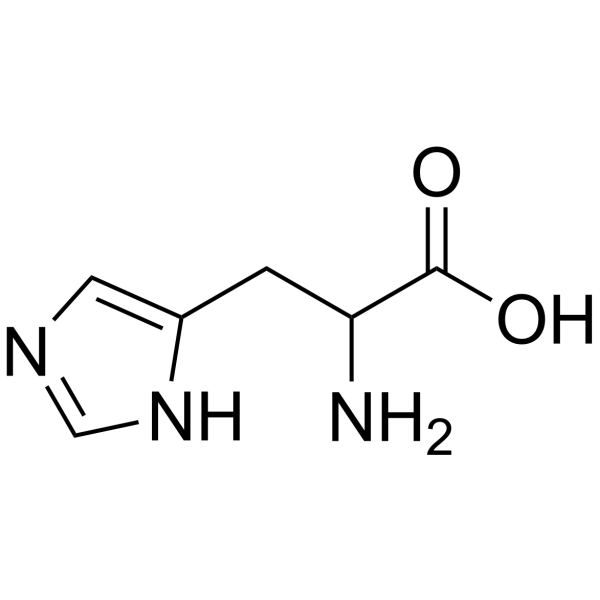 |
DL-Histidine
CAS:4998-57-6 |