| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
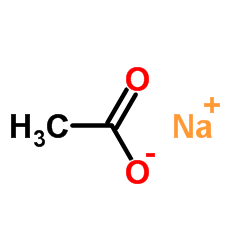 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
L-cysteine
CAS:52-90-4 |
|
 |
Tellurium
CAS:13494-80-9 |
|
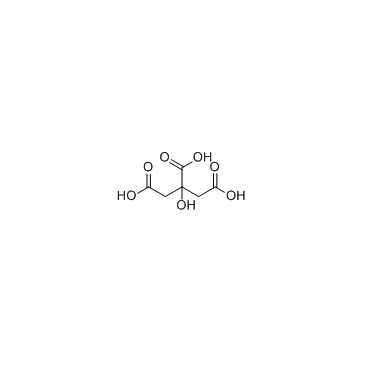 |
Citric Acid
CAS:77-92-9 |
|
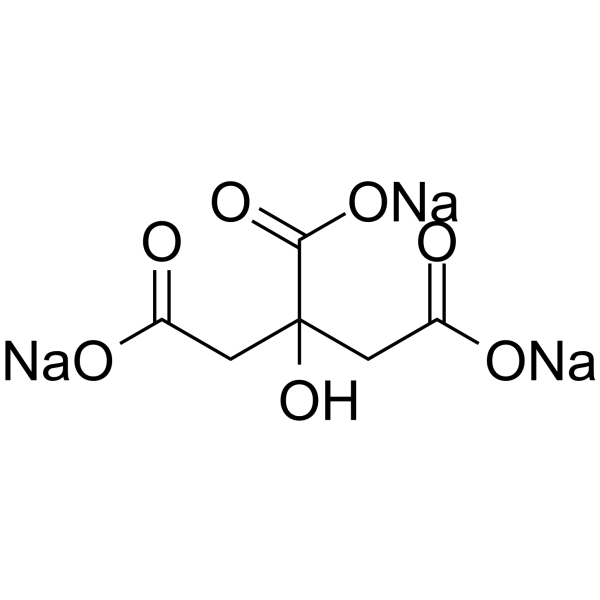 |
Sodium citrate
CAS:68-04-2 |
|
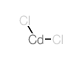 |
Cadmium chloride
CAS:10108-64-2 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
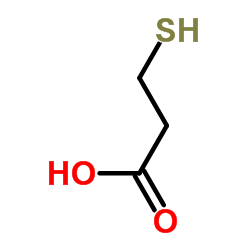 |
3-Mercaptopropionic acid
CAS:107-96-0 |