tricosanoic acid tryptamide
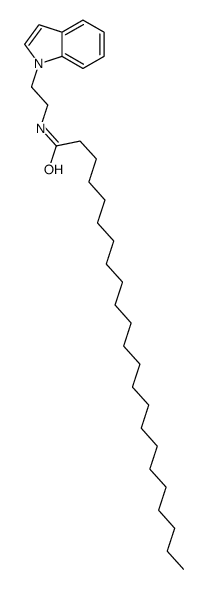
tricosanoic acid tryptamide structure
|
Common Name | tricosanoic acid tryptamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 152766-93-3 | Molecular Weight | 496.81100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C33H56N2O | Melting Point | 116-120ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
SPREDs (Sprouty related proteins with EVH1 domain) promote self-renewal and inhibit mesodermal differentiation in murine embryonic stem cells.
Dev. Dyn. 244(4) , 591-606, (2015) Pluripotency, self-renewal, and differentiation are special features of embryonic stem (ES) cells, thereby providing valuable perspectives in regenerative medicine. Developmental processes require a fine-tuned organization, mainly regulated by the well-known ... |
|
|
Regulation of phagocytosis and cytokine secretion by store-operated calcium entry in primary isolated murine microglia.
Cell. Signal. 27(1) , 177-86, (2015) Microglia are immune effector cells in the central nervous system that participate in tissue repair, inflammatory responses, and neuronal degeneration. The most important signaling factor in the differentiation of immune-active cells after stimulation is the ... |
|
|
Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells toward dopaminergic neurons using recombinant LMX1A factor.
Mol. Biotechnol. 57(2) , 184-94, (2015) Direct differentiation of dopaminergic (DA) neurons from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) in the absence of gene manipulation is the most desired alternative to clinical treatment of Parkinson disease. Protein transduction-based methods could be efficient... |
|
|
Blood-brain barrier permeable gold nanoparticles: an efficient delivery platform for enhanced malignant glioma therapy and imaging.
Small 10(24) , 5137-50, (2014) The blood-brain barrier (BBB) remains a formidable obstacle in medicine, preventing efficient penetration of chemotherapeutic and diagnostic agents to malignant gliomas. Here, a transactivator of transcription (TAT) peptide-modified gold nanoparticle platform... |
|
|
Targeted sequencing of large genomic regions with CATCH-Seq.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e111756, (2014) Current target enrichment systems for large-scale next-generation sequencing typically require synthetic oligonucleotides used as capture reagents to isolate sequences of interest. The majority of target enrichment reagents are focused on gene coding regions ... |
|
|
Dynein light intermediate chains maintain spindle bipolarity by functioning in centriole cohesion.
J. Cell Biol. 207(4) , 499-516, (2014) Cytoplasmic dynein 1 (dynein) is a minus end-directed microtubule motor protein with many cellular functions, including during cell division. The role of the light intermediate chains (LICs; DYNC1LI1 and 2) within the complex is poorly understood. In this pap... |
|
|
Development of a mouse model for chronic cat allergen-induced asthma.
Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 165(3) , 195-205, (2015) Allergic asthma is a chronic inflammatory airway disease caused by exposure to airborne allergens. In order to develop novel therapies for allergic asthma, models that are relevant to human disease are needed.Female BALB/c mice were presensitised subcutaneous... |
|
|
Impact of an autologous oxygenating matrix culture system on rat islet transplantation outcome.
Biomaterials 52 , 180-8, (2015) Disruption of the pancreatic islet environment combined with the decrease in oxygen supply that occurs during isolation leads to poor islet survival. The aim of this study was to validate the benefit of using a plasma-based scaffold supplemented with perfluor... |
|
|
Activation of intracellular angiotensin AT₂ receptors induces rapid cell death in human uterine leiomyosarcoma cells.
Clin. Sci. 128(9) , 567-78, (2015) The presence of angiotensin type 2 (AT₂) receptors in mitochondria and their role in NO generation and cell aging were recently demonstrated in various human and mouse non-tumour cells. We investigated the intracellular distribution of AT₂ receptors including... |
|
|
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of blood coagulation activation of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel plus dextran-based vascular grafts.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 103(4) , 1366-79, (2015) Polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel (PVA) is a water-soluble synthetic polymer that is commonly used in biomedical applications including vascular grafting. It was argued that the copolymerization of PVA with dextran (Dx) can result in improvement of blood-biomaterial... |