Zeatin
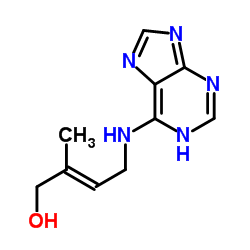
Zeatin structure
|
Common Name | Zeatin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13114-27-7 | Molecular Weight | 219.24 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 395.0±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 192.7±30.7 °C | |
|
Adaptive significance of gall formation for a gall-inducing aphids on Japanese elm trees.
J. Insect Physiol. 72 , 43-51, (2015) Insect galls are abnormal plant tissues induced by external stimuli from parasitizing insects. It has been suggested that the stimuli include phytohormones such as auxin and cytokinins produced by the insects. In our study on the role of hormones in gall indu... |
|
|
The plant hormone zeatin riboside inhibits T lymphocyte activity via adenosine A2A receptor activation.
Cell. Mol. Immunol. 12(1) , 107-12, (2015) Cytokinins are plant hormones that play an integral role in multiple aspects of plant growth and development. The biological functions of cytokinins in mammalian systems are, however, largely uncharacterized. The naturally occurring cytokinin zeatin riboside ... |
|
|
Altered metabolism of gut microbiota contributes to chronic immune activation in HIV-infected individuals.
Mucosal Immunol. 8 , 760-72, (2015) Altered interplay between gut mucosa and microbiota during treated HIV infection may possibly contribute to increased bacterial translocation and chronic immune activation, both of which are predictors of morbidity and mortality. Although a dysbiotic gut micr... |
|
|
Optimizing regeneration condition in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.).
Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 11 , 1009-1014, (2008) In this study, multiple shoot induction and whole plant regeneration from decapitated embryo axes of three chick peal genotypes including MCC252, MCC283 and MCC505 were evaluated on modified Murashige and Skoog's medium (MMS) which, its vitamins were replaced... |
|
|
Cytokinins inhibit epiphyllous plantlet development on leaves of Bryophyllum (Kalanchoë) marnierianum.
J. Exp. Bot. 57 , 4089-4098, (2006) When leaves of Bryophyllum marnierianum are detached from the plant, plantlets develop from primordia located at their margins. Leaves excised with a piece of stem attached do not produce plantlets. Severing the major leaf veins overcomes the inhibitory effec... |
|
|
Integration of shot-gun proteomics and bioinformatics analysis to explore plant hormone responses.
BMC Bioinformatics 13 Suppl 15 , S8, (2012) Multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT)-based shot-gun proteomics has been proven to be an effective platform for functional proteomics. In particular, the various sample preparation methods and bioinformatics tools can be integrated to im... |
|
|
Determination of genetic stability in long-term somatic embryogenic cultures and derived plantlets of cork oak using microsatellite markers.
Tree Physiol. 26 , 1145-1152, (2006) Microsatellites were used to test genetic stability in somatic embryos (SE) of Quercus suber L. The SE were obtained by a simple somatic embryogenesis protocol: leaf explants from two adult plants (QsG0, QsG5) and from two juvenile plants (QsGM1, QsGM2) were ... |
|
|
An efficient protocol for high-frequency direct multiple shoot regeneration from internodes of peppermint (Mentha x piperita).
Nat. Prod. Commun. 5 , 1945-1946, (2010) A simple, repeatable and efficient protocol for direct multiple shoot regeneration from internodal explants has been defined in peppermint (Mentha x piperita var. Indus). In vitro regenerated shoots of peppermint were excised into 4 to 8 mm long internodes an... |
|
|
Coexpression analysis of tomato genes and experimental verification of coordinated expression of genes found in a functionally enriched coexpression module.
DNA Res. 17 , 105-16, (2010) Gene-to-gene coexpression analysis is a powerful approach to infer the function of uncharacterized genes. Here, we report comprehensive identification of coexpression gene modules of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and experimental verification of coordinated e... |
|
|
Draft genome sequence of the rubber tree Hevea brasiliensis.
BMC Genomics 14 , 75, (2013) Hevea brasiliensis, a member of the Euphorbiaceae family, is the major commercial source of natural rubber (NR). NR is a latex polymer with high elasticity, flexibility, and resilience that has played a critical role in the world economy since 1876.Here, we r... |