(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
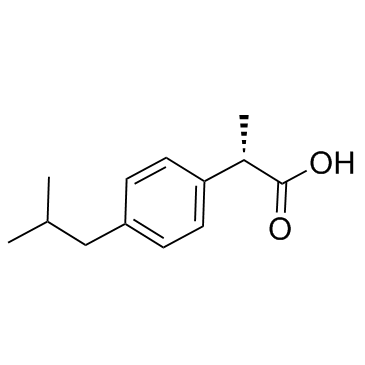
(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen structure
|
Common Name | (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51146-56-6 | Molecular Weight | 206.281 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 319.6±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H18O2 | Melting Point | 49-53ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 216.7±14.4 °C | |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
The advantages and limitations of the analgesics available for control of postoperative pain after a dental procedure.
SAAD Dig. 29 , 70-81, (2013)
|
|
|
Pegylation improves the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of small-molecule drugs hydrolyzable by esterases: a study of phospho-Ibuprofen.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 351(1) , 61-6, (2014) Esterase hydrolysis of drugs can accelerate their elimination, thereby limiting their efficacy. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) covalently attached to drugs (pegylation) is known to improve the efficiency of many drugs. Using as a test agent the novel phospho-ibupr... |
|
|
Hologram QSAR model for the prediction of human oral bioavailability.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 7738-45, (2007) A drug intended for use in humans should have an ideal balance of pharmacokinetics and safety, as well as potency and selectivity. Unfavorable pharmacokinetics can negatively affect the clinical development of many otherwise promising drug candidates. A varie... |
|
|
An investigation into the drug release from ibuprofen matrix tablets with ethylcellulose and some poly-acrylate polymers.
Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 27(3) , 495-503, (2014) This study was performed to achieve sustained-release Ibuprofen matrix tablets with a zero-order release kinetic while most of the previous formulations have shown Higuchi release kinetic. Considering the results from previous studies, ethyl cellulose, Carbop... |
|
|
Influence of beta-cyclodextrin and chitosan in the formulation of a colon-specific drug delivery system.
Drug Res. (Stuttg.) 63(12) , 657-62, (2013) The increase in diseases of the colon underscores the need to develop cost-effective site-directed therapies. We formulated a polysaccharide-based matrix system that could release ibuprofen under conditions simulating those in the colon by employing a wet gra... |
|
|
Effects of ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxen, and piroxicam on the course of pregnancy and pregnancy outcome: a prospective cohort study.
BJOG 120(8) , 948-59, (2013) To investigate the individual effects of ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxen, and piroxicam on pregnancy outcome.Cohort study.Norwegian population.A total of 90 417 women and singleton child pairs.The Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study and Medical Birth Regi... |
|
|
Gelatine enhances drug dispersion in alginate bilayer film via the formation of crystalline microaggregates.
Int. J. Pharm. 454(1) , 99-106, (2013) In our previous study, a novel alginate-based bilayer film for slow-release wound dressings was successfully developed. We found that alginate alone yielded poor films; however, the addition of gelatine had significantly enhanced the drug dispersion as well a... |
|
|
Chamazulene carboxylic acid and matricin: a natural profen and its natural prodrug, identified through similarity to synthetic drug substances.
J. Nat. Prod. 69 , 1041-5, (2006) Chamazulene carboxylic acid (1) is a natural profen with anti-inflammatory activity and a degradation product of proazulenic sesquiterpene lactones, e.g., matricin. Both 1 and proazulenes occur in chamomile (Matricaria recutita), yarrow (Achillea millefolium)... |
|
|
Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutically active and endocrine disrupting compounds in Singapore's marine environment: influence of hydrodynamics and physical-chemical properties.
Environ. Pollut. 182 , 1-8, (2013) The fate and exposure risks of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) and endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in marine environments are not well-understood. In this study we developed a multi-residue analytical method for quantifying concentrations of f... |