H-TRP-NH2 HCL
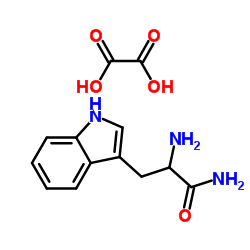
H-TRP-NH2 HCL structure
|
Common Name | H-TRP-NH2 HCL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5022-65-1 | Molecular Weight | 293.275 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 498.7ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H15N3O5 | Melting Point | 250ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 255.4ºC | |
|
Solvent effects on the fluorescence quenching of tryptophan by amides via electron transfer. Experimental and computational studies.
J. Phys. Chem. B 113 , 2572-2577, (2009) Hybrid quantum mechanical/molecular mechanics (QM-MM) calculations [Callis and Liu, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 4248-4259] make a strong case that the large variation in tryptophan (Trp) fluorescence yields in proteins is explained by ring-to-backbone amide e... |
|
|
Peptide synthesis catalyzed by an antibody containing a binding site for variable amino acids.
Science 265 , 234, (1994) Monoclonal antibodies, induced with a phosphonate diester hapten, catalyzed the coupling of p-nitrophenyl esters of N-acetyl valine, leucine, and phenylalanine with tryptophan amide to form the corresponding dipeptides. All possible stereoisomeric combination... |
|
|
Metal-enhanced Intrinsic Fluorescence of Proteins on Silver Nanostructured Surfaces towards Label-Free Detection.
J. Phys. Chem. C Nanomater. Interfaces 112 , 17957-17963, (2008) In recent years metal-enhanced fluorescence (MEF) using silver particles has been reported for a number of fluorophores emitting at visible wavelengths. However it was generally thought that silver particles would always quench fluorescence at shorter wavelen... |
|
|
Peptide sequence and conformation strongly influence tryptophan fluorescence.
Biophys. J. 94 , 2280-2287, (2008) This article probes the denatured state ensemble of ribonuclease Sa (RNase Sa) using fluorescence. To interpret the results obtained with RNase Sa, it is essential that we gain a better understanding of the fluorescence properties of tryptophan (Trp) in pepti... |
|
|
Stability decrease of RNA double helices by phenylalanine-, tyrosine- and tryptophane-amides. Analysis in terms of site binding and relation to melting proteins.
Nucleic Acids Res. 10(19) , 6163-76, (1982) The amides of L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine and L-tryptophane decrease the melting temperatures tm of poly(A)*poly(U) and poly(I)*poly(C) double helices at low concentrations (1 mM), whereas high concentrations finally lead to an increase of tm. This dependence... |
|
|
Tryptophanamide formation by Escherichia coli tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase.
Eur. J. Biochem. 146(1) , 201-9, (1985) When tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli is allowed to react with L-tryptophan and ATP-Mg in the presence of inorganic pyrophosphatase, the fluorescence change of the reaction mixture reveals three or four sequential processes, depending on the... |
|
|
Tryptophan as a probe for acid-base equilibria in peptides.
Biopolymers 71(5) , 569-76, (2003) We present results of time resolved fluorescence measurements performed in Tryptophan (Trp) derivatives and Trp-containing peptides in the pH range 3.0-11.0. For each compound a set of decay profiles measured in a given range of pH values was examined as a wh... |
|
|
Pressure effects on tryptophan and its derivatives.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 269(3) , 681-6, (2000) The high pressure effects on fluorescence of free tryptophan (Trp) and its derivatives, N-acetyl-tryptophan (AT), N-acetyl-tryptophanamide (NATA), tryptophanamide (TA), and tryptophan, containing 6-polypeptides in aqueous solution, were investigated in a pres... |