D-Cycloserine
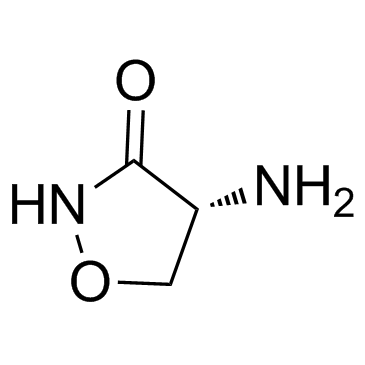
D-Cycloserine structure
|
Common Name | D-Cycloserine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 68-41-7 | Molecular Weight | 102.092 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 267ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6N2O2 | Melting Point | 147ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Heterogeneity of clinical and environmental isolates of Mycobacterium fortuitum using repetitive element sequence-based PCR: municipal water an unlikely source of community-acquired infections.
Epidemiol. Infect. 142(10) , 2057-64, (2014) M. fortuitum is a rapidly growing mycobacterium associated with community-acquired and nosocomial wound, soft tissue, and pulmonary infections. It has been postulated that water has been the source of infection especially in the hospital setting. The aim of t... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Simple and accurate quantitative analysis of 20 anti-tuberculosis drugs in human plasma using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 9-16, (2014) A simple and accurate liquid chromatography (LC)-tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) method for the quantitation of 20 anti-tuberculosis (anti-TB) drugs in human plasma, was developed as a tool for therapeutic drug monitoring. Two protein precipitation methods w... |
|
|
Neural computational prediction of oral drug absorption based on CODES 2D descriptors.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45 , 930-40, (2010) A neural model based on a numerical molecular representation using CODES program to predict oral absorption of any structure is described. This model predicts both high and low-absorbed compounds with a global accuracy level of 74%. CODES/ANN methodology show... |
|
|
Prediction of drug intestinal absorption by new linear and non-linear QSPR.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 , 218-28, (2011) In order to minimize the high attrition rate that usually characterizes drug research and development projects, current medicinal chemists aim to characterize both pharmacological and ADME profiles at the beginning of drug R&D initiatives. Thus, the developme... |
|
|
Comparative study of the effects of antituberculosis drugs and antiretroviral drugs on cytochrome P450 3A4 and P-glycoprotein.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(6) , 3168-76, (2014) Predicting drug-drug interactions (DDIs) related to cytochrome P450 (CYP), such as CYP3A4 and one of the major drug transporters, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), is crucial in the development of future chemotherapeutic regimens to treat tuberculosis (TB) and TB/AIDS c... |
|
|
Tau-mediated NMDA receptor impairment underlies dysfunction of a selectively vulnerable network in a mouse model of frontotemporal dementia.
J. Neurosci. 34(49) , 16482-95, (2014) Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a neurodegenerative behavioral disorder that selectively affects the salience network, including the ventral striatum and insula. Tau mutations cause FTD, but how mutant tau impairs the salience network is unknown. Here, we ad... |
|
|
Stereomicroscopic 3D-pattern profiling of murine and human intestinal inflammation reveals unique structural phenotypes.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7577, (2015) Histology is fundamental to assess two-dimensional intestinal inflammation; however, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) are often indistinguishable microscopically on the basis of mucosal biopsies. Here, we use stereomicroscopy (SM) to rapidly profile the ent... |
|
|
Resuscitation-promoting factors are cell wall-lytic enzymes with important roles in the germination and growth of Streptomyces coelicolor.
J. Bacteriol. 197(5) , 848-60, (2015) Dormancy is a common strategy adopted by bacterial cells as a means of surviving adverse environmental conditions. For Streptomyces bacteria, this involves developing chains of dormant exospores that extend away from the colony surface. Both spore formation a... |