20(S)-Hydroxycholesterol
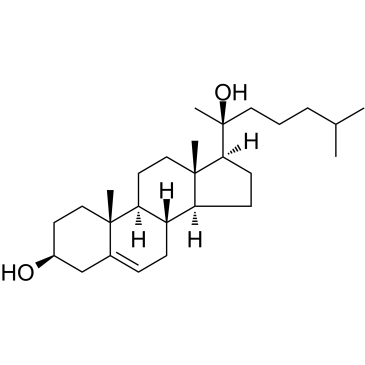
20(S)-Hydroxycholesterol structure
|
Common Name | 20(S)-Hydroxycholesterol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 516-72-3 | Molecular Weight | 402.65 | |
| Density | 1.03g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 512.3ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H46O2 | Melting Point | 136-137ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 213.1ºC | |
|
In vitro osteoinductive effects of hydroxycholesterol on human adipose-derived stem cells are mediated through the hedgehog signaling pathway.
Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 134(5) , 960-8, (2014) Human adipose-derived stem cells have been identified as a potential source of cells for use in bone tissue engineering because of their ready availability, ease of harvest, and susceptibility to osteogenic induction. The authors have previously demonstrated ... |
|
|
Conversion of exogenous cholesterol into glycoalkaloids in potato shoots, using two methods for sterol solubilisation.
PLoS ONE 8 , e82955, (2013) Steroidal glycoalkaloids (SGA) are toxic secondary metabolites naturally occurring in the potato, as well as in certain other Solanaceous plant species, such as tomato, eggplant and pepper. To investigate the steroidal origin of SGA biosynthesis, cut potato s... |
|
|
Oxpholipin 11D: an anti-inflammatory peptide that binds cholesterol and oxidized phospholipids.
PLoS ONE 5 , e10181, (2010) Many gram-positive bacteria produce pore-forming exotoxins that contain a highly conserved, 12-residue domain (ECTGLAWEWWRT) that binds cholesterol. This domain is usually flanked N-terminally by arginine and C-terminally by valine. We used this 14-residue se... |
|
|
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage by mitochondria from the human placenta. Studies using hydroxycholesterols as substrates.
J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 42(8) , 883-90, (1992) The side-chain cleavage of cholesterol by cytochrome P-450scc in mitochondria from the human placenta was studied using hydroxycholesterol substrates and intermediates of the reaction. 25-Hydroxycholesterol inhibited 3 beta-hydroxy-5-pregnen-20-one (pregnenol... |
|
|
Modulators of the hedgehog signaling pathway.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 6613-24, (2010) Since its discovery by C. Nüsslein-Volhard and E. F. Wieschaus, hedgehog (hh) signaling has come a long way. Today it is regarded as a key regulator in embryogenesis where it governs processes like cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue patterning. F... |
|
|
An early steroidogenic defect in hormone-induced Leydig cell desensitization.
J. Steroid Biochem. 21(3) , 265-77, (1984) To define the nature of the lesion of the early steroidogenic pathway (prior to pregnenolone formation) in gonadotropin-induced desensitization of rat testicular Leydig cells, we evaluated cholesterol side-chain cleavage activity in isolated mitochondria by m... |
|
|
Restoration effects of exogenous luteinizing hormone on the testicular steroidogenesis and Leydig cell ultrastructure.
Endocrinology 117(5) , 1779-87, (1985) In the present study, we explored the restoration effects of exogenous LH on Leydig cell ultrastructure and testicular steroidogenesis in rats that were deprived of endogenous LH via treatment with testosterone-17 beta-estradiol-filled Silastic implants for 1... |
|
|
Osteogenic oxysterol, 20(S)-hydroxycholesterol, induces notch target gene expression in bone marrow stromal cells.
J. Bone Miner Res. 25(4) , 782-95, (2010) We previously reported that specific oxysterols stimulate osteogenic differentiation of pluripotent bone marrow stromal cells (MSCs) through activation of hedgehog (Hh) signaling and may serve as potential future therapies for intervention in osteopenia and o... |
|
|
Heterogeneous pools of cholesterol side-chain cleavage activity in adrenal mitochondria from ACTH-treated rats: differential responses to different reducing precursors.
Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 73(2-3) , 123-34, (1990) Side-chain cleavage (SCC) of endogenous cholesterol in adrenal mitochondria isolated from ACTH-treated rats indicates that the size of the reactive cholesterol pool depends on the reducing precursor. At optimal concentrations of reductant, this pool was typic... |
|
|
The regulation of steroidogenesis is different in the two types of ovine luteal cells.
Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 63(3) , 240-8, (1985) Ovine luteal tissue contains two distinct steroidogenic cell types, small (8-20 microns) and large (greater than 20 microns), which differ based on morphological and biochemical criteria. Unstimulated small cells secrete low levels of progesterone, respond to... |