Sodium molybdate
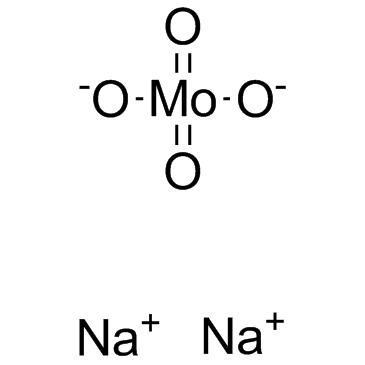
Sodium molybdate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium molybdate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7631-95-0 | Molecular Weight | 205.917 | |
| Density | 3.78 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 100ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | MoNa2O4 | Melting Point | 687 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Inhibition of invasion by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibitors through dysregulation of actin re-organisation via down-regulation of WAVE2
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 464 , 275-80, (2015) Cancer cell invasion is a critical phenomenon in cancer pathogenesis. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) has been reported to regulate cancer cell invasion both negatively and positively. Thus, the net effect of GSK-3β on invasion is unclear. In this report... |
|
|
SPECHT - single-stage phosphopeptide enrichment and stable-isotope chemical tagging: quantitative phosphoproteomics of insulin action in muscle.
J. Proteomics 114 , 48-60, (2015) The study of cellular signaling remains a significant challenge for translational and clinical research. In particular, robust and accurate methods for quantitative phosphoproteomics in tissues and tumors represent significant hurdles for such efforts. In the... |
|
|
Destabilisation of dimeric 14-3-3 proteins as a novel approach to anti-cancer therapeutics.
Oncotarget 6 , 14522-36, (2015) 14-3-3 proteins play a pivotal role in controlling cell proliferation and survival, two commonly dysregulated hallmarks of cancers. 14-3-3 protein expression is enhanced in many human cancers and correlates with more aggressive tumors and poor prognosis, sugg... |
|
|
Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta induces apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe by disrupting centrosome regulation in cancer cells.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13249, (2015) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β) has been investigated as a therapeutic target for numerous human diseases including cancer because of their diverse cellular functions. Although GSK-3β inhibitors have been investigated as anticancer reagents, precise ... |
|
|
Compromising the 19S proteasome complex protects cells from reduced flux through the proteasome.
Elife 4 , (2015) Proteasomes are central regulators of protein homeostasis in eukaryotes. Proteasome function is vulnerable to environmental insults, cellular protein imbalance and targeted pharmaceuticals. Yet, mechanisms that cells deploy to counteract inhibition of this ce... |
|
|
Total inhibition of (1)O2-induced oxidative damage to guanine bases of DNA/RNA by turmeric extracts.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 452(3) , 515-9, (2014) The guanine base of nucleic acids is known to be very reactive towards degradation by (1)O2-induced oxidative stress. Oxidative reactions of DNA are linked to many human diseases including cancer. Among the various forms of reactive O2 species (OH, (1)O2 or O... |
|
|
Few-layered MoSe2 nanosheets as an advanced electrode material for supercapacitors.
Dalton Trans. 44 , 15491-8, (2015) We report the synthesis of few-layered MoSe2 nanosheets using a facile hydrothermal method and their electrochemical charge storage behavior. A systematic study of the structure and morphology of the as-synthesized MoSe2 nanosheets was performed. The downward... |
|
|
Large-scale analysis of lysine SUMOylation by SUMO remnant immunoaffinity profiling.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5409, (2014) Small ubiquitin-related modifiers (SUMO) are evolutionarily conserved ubiquitin-like proteins that regulate several cellular processes including cell cycle progression, intracellular trafficking, protein degradation and apoptosis. Despite the importance of pr... |
|
|
Using contemporary liquid chromatography theory and technology to improve capillary gradient ion-exchange separations.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1370 , 63-9, (2014) The gradient-performance limits of capillary ion chromatography have been assessed at maximum system pressure (34.5 MPa) using capillary columns packed with 4.1 μm macroporous anion-exchange particles coated with 65 nm positively-charged nanobeads. In analogy... |
|
|
Loss of giant obscurins from breast epithelium promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, tumorigenicity and metastasis.
Oncogene 34 , 4248-59, (2015) Obscurins, encoded by the single OBSCN gene, are giant cytoskeletal proteins with structural and regulatory roles. The OBSCN gene is highly mutated in different types of cancers. Loss of giant obscurins from breast epithelial cells confers them with a surviva... |