Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
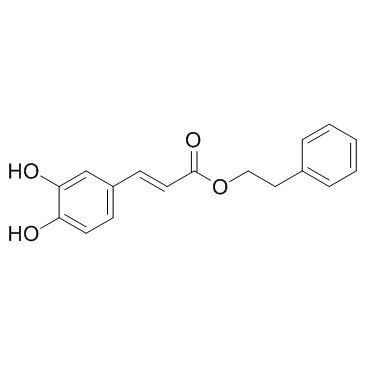
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester structure
|
Common Name | Caffeic acid phenethyl ester | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104594-70-9 | Molecular Weight | 284.306 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 498.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H16O4 | Melting Point | 129 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 185.1±22.2 °C | |
|
Ganglioside GM3 is required for caffeic acid phenethyl ester-induced megakaryocytic differentiation of human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cells.
Biochem. Cell Biol. 92(4) , 243-9, (2014) The human chronic myelogenous cell line K562 has been used extensively as a model for the study of leukemia differentiation. We show here that treatment of K562 cells with caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) induced a majority of cells to differentiate toward... |
|
|
Inhibition of COX-2-mediated eicosanoid production plays a major role in the anti-inflammatory effects of the endocannabinoid N-docosahexaenoylethanolamine (DHEA) in macrophages.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(1) , 24-37, (2014) N-docosahexaenoylethanolamine (DHEA) is the ethanolamine conjugate of the long-chain polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic (DHA; 22: 6n-3). Its concentration in animal tissues and human plasma increases when diets rich in fish or krill oil are consum... |
|
|
Effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on wound healing in calvarial defects.
Acta Odontol. Scand. 73(1) , 21-7, (2014) The aim of this study is to analyze histologically the effect of CAPE on bone healing of Critical Size Defect (CSD) in rat calvaria.Thirty-two 3-month-old male rats were used. The animals were randomly divided into four groups. Group A received isotonic salin... |
|
|
Dual role of superoxide dismutase 2 induced in activated microglia: oxidative stress tolerance and convergence of inflammatory responses.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 22805-17, (2015) Microglia are activated quickly in response to external pathogens or cell debris and clear these substances via the inflammatory response. However, excessive activation of microglia can be harmful to host cells due to the increased production of reactive oxyg... |
|
|
Activation of neutral-sphingomyelinase, MAPKs, and p75 NTR-mediating caffeic acid phenethyl ester-induced apoptosis in C6 glioma cells.
J. Biomed. Sci. 21 , 61, (2014) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), a component of propolis, is reported to possess anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-viral, and anti-tumor activities. Previously, our laboratory demonstrated the in vitro and in vivo bioactivity of CAPE and addressed t... |
|
|
Caffeic Acid phenethyl ester and ethanol extract of propolis induce the complementary cytotoxic effect on triple-negative breast cancer cell lines.
Molecules 20 , 9242-62, (2015) Chemotherapy of breast cancer could be improved by bioactive natural substances, which may potentially sensitize the carcinoma cells' susceptibility to drugs. Numerous phytochemicals, including propolis, have been reported to interfere with the viability of c... |
|
|
Innate signaling mechanisms controlling Mycobacterium chelonae-mediated CCL2 and CCL5 expression in macrophages.
J. Microbiol. 53 , 864-74, (2015) Mycobacterium chelonae (Mch) is an atypical rapidly growing mycobacterium (RGM) that belongs to the M. chelonae complex, which can cause a variety of human infections. During this type of mycobacterial infection, macrophage-derived chemokines play an importan... |
|
|
Effects of natural nuclear factor-kappa B inhibitors on anticancer drug efflux transporter human P-glycoprotein.
Biomed. Pharmacother. 70 , 140-5, (2015) Drug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein plays an important role in cancer chemotherapy. The nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) transcription factors play critical roles in development and progression of cancer. In this study, the effects of natural compounds that can i... |
|
|
Caffeic Acid phenethyl ester: consequences of its hydrophobicity in the oxidative functions and cytokine release by leukocytes.
Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014 , 793629, (2014) Numerous anti-inflammatory properties have been attributed to caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), an active component of propolis. NADPH oxidases are multienzymatic complexes involved in many inflammatory diseases. Here, we studied the importance of the CAPE... |
|
|
Antibiofilm Activity of Chilean Propolis on Streptococcus mutans Is Influenced by the Year of Collection.
Biomed Res. Int. 2015 , 291351, (2015) The chemical composition of propolis varies according to factors that could have an influence on its biological properties. Polyphenols from propolis have demonstrated an inhibitory effect on Streptococcus mutans growth. However, it is not known if different ... |