N-Acetyl-DL-aspartic acid
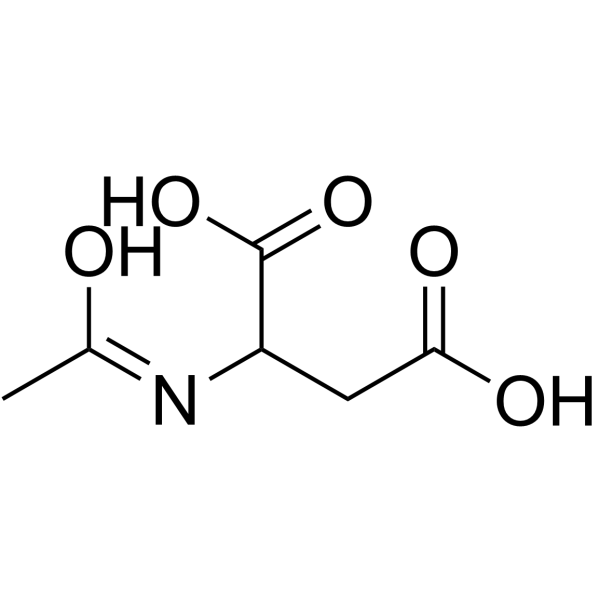
N-Acetyl-DL-aspartic acid structure
|
Common Name | N-Acetyl-DL-aspartic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2545-40-6 | Molecular Weight | 175.139 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 425.3±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9NO5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 211.0±25.9 °C | |
|
Structural variation governs substrate specificity for organic anion transporter (OAT) homologs. Potential remote sensing by OAT family members.
J. Biol. Chem. 282 , 23841-53, (2007) Organic anion transporters (OATs, SLC22) interact with a remarkably diverse array of endogenous and exogenous organic anions. However, little is known about the structural features that determine their substrate selectivity. We examined the substrate binding ... |
|
|
Functional changes in the frontal cortex in Parkinson's disease using a rat model.
J. Clin. Neurosci. 17 , 628-633, (2010) In recent years, investigations of the pathologic mechanism of Parkinson's disease (PD) have mainly concentrated on the basal ganglia. However, recent studies have confirmed that pathological changes in PD are accompanied by functional motor changes of the ce... |
|
|
[Canavan disease or N-acetyl aspartic aciduria: a case report].
Arch. Pediatr. 14 , 173-176, (2007) Canavan disease or N-acetyl aspartic aciduria, is an autosomal recessive leukodystrophy characterized by spongy degeneration of brain. The disease is an inborn error of metabolism caused by aspartoacylase deficiency resulting from accumulation of N-acetyl asp... |
|
|
Excitatory acidic amino acids and the cation content and sodium ion flux of isolated tissues from the brain.
Biochem. J. 108 , 269-274, (1968) 1. Sample from the neocortex and piriform cortex of guinea pigs and rats were incubated in inulin-containing glucose-saline. Their intracellular (non-inulin) space contained 19-27muequiv. of Na(+)/g. of original tissue. These values were stable between 30 and... |