poly(n-isopropyl acrylamide)
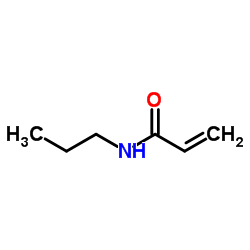
poly(n-isopropyl acrylamide) structure
|
Common Name | poly(n-isopropyl acrylamide) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 25189-55-3 | Molecular Weight | 113.158 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 234.2±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11NO | Melting Point | 96 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 126.0±4.8 °C | |
|
Label-free detection of low protein concentration in solution using a novel colorimetric assay.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 49 , 133-8, (2013) Dual pH and temperature sensitive microgel-based etalons were fabricated by sandwiching a "monolithic" microgel layer between two semitransparent, Au layers. The devices exhibit visual color and multipeak reflectance spectra, both of which primarily depend on... |
|
|
Mechanistic insights into amplification of specific ion effect in water-nonaqueous solvent mixtures.
J. Phys. Chem. B 117(8) , 2535-44, (2013) Ethylene glycol (EG) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) can act as both hydrogen-bond donors and acceptors in the formation of solvent complexes with water molecules. In the present work, we have systematically investigated the ion-specific lower critical solution ... |
|
|
Tailoring enzyme activity and stability using polymer-based protein engineering.
Biomaterials 34(30) , 7437-43, (2013) Polymer-based protein engineering (PBPE) offers an attractive method to predictably modify and enhance enzyme structure and function. Using polymers that respond to stimuli such as temperature and pH, enzyme activity and stability can be predictably modified ... |
|
|
Polysaccharides as a source of advanced materials: cellulose hollow microspheres for drug delivery in cancer therapy.
J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 384(1) , 198-206, (2012) Biocompatible hollow poly(methyl acrylic acid-co-N-isopropylacrylamide-co-ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate)@cellulose succinate (P(MAA-co-NIPAAM-co-EGDMA)@CS) microspheres have been synthesized by employing uniform silica-MPS microspheres as template. Silica sph... |
|
|
Incorporation of biphasic calcium phosphate microparticles in injectable thermoresponsive hydrogel modulates bone cell proliferation and differentiation
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 110 , 120-9, (2013) To provide osteoblast cells with a three-dimensional environment closer to bone matrix, an engineered construct mimicking bone components have been designed and evaluated. A biocompatible injectable thermo-responsive hydrogel, hyaluronic acid-g-chitosan-g-pol... |
|
|
Preparation and friction force microscopy measurements of immiscible, opposing polymer brushes.
J. Vis. Exp. (94) , doi:10.3791/52285, (2014) Solvated polymer brushes are well known to lubricate high-pressure contacts, because they can sustain a positive normal load while maintaining low friction at the interface. Nevertheless, these systems can be sensitive to wear due to interdigitation of the op... |
|
|
New directions in thermoresponsive polymers.
Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(17) , 7214-43, (2013) Interest in thermoresponsive polymers has steadily grown over many decades, and a great deal of work has been dedicated to developing temperature sensitive macromolecules that can be crafted into new smart materials. However, the overwhelming majority of prev... |
|
|
ABC triblock terpolymers exhibiting both temperature- and pH-sensitive micellar aggregation and gelation in aqueous solution.
Langmuir 28(51) , 17785-94, (2012) Two poly(ethylene-alt-propylene)-b-poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) (PEP-PEO-P(NIPAm-co-AA)) triblock terpolymers were synthesized by a combination of anionic and RAFT polymerizations, followed by acid hydrolysis. Micellar ag... |
|
|
Preparation and characterization of pH- and temperature-responsive nanocomposite double network hydrogels.
Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 33(4) , 1951-7, (2013) A methodology is described for the preparation of pH- and temperature-responsive double network (DN) hydrogels with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) as a tightly crosslinked 1st network, polyacrylic acid (PAA) as a loosely crosslinked 2nd network and grap... |
|
|
Immobilization of bacterial luciferase into poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) film for electrochemical control of a bioluminescence reaction.
Anal. Sci. 28(10) , 1013-5, (2012) A poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) film was modified on an indium-tin oxide electrode in order to immobilize bacterial luciferase (BL) on the electrode surface. By using the modified electrode, flavin mononucleotide (FMN) was electrochemically reduced to FMNH(2), ... |