lignosulfonic acid, calcium salt
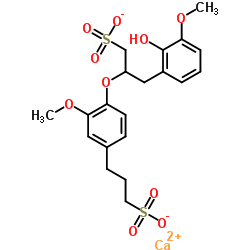
lignosulfonic acid, calcium salt structure
|
Common Name | lignosulfonic acid, calcium salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 8061-52-7 | Molecular Weight | 528.607 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H24CaO10S2 | Melting Point | 130 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Effects of soybean hulls and lignosulfonate-treated soybean meal on ruminal fermentation in lactating dairy cows.
J. Dairy Sci. 77(4) , 1070-83, (1994) Four Holstein cows were used in a 4 x 4 Latin square design to investigate the effects of soybean hulls and lignosulfonate-treated soybean meal on ruminal fermentation and nutrient passage to the duodenum. Diets contained 32% corn silage, 19.8% alfalfa-grass ... |
|
|
Combination of three-stage sink-float method and selective flotation technique for separation of mixed post-consumer plastic waste.
Waste Manag. 28(3) , 475-83, (2008) The aim of this research was to separate the different plastics of a mixed post-consumer plastic waste by the combination of a three-stage sink-float method and selective flotation. By using the three-stage sink-float method, six mixed-plastic wastes, belongi... |
|
|
Degradation of calcium lignosulfonate using gamma-ray irradiation.
Chemosphere 57(9) , 1181-7, (2004) Gamma-ray irradiation was proven to be a promising means for the removal of calcium lignosulfonate (CaLS). At a dose rate of 55Gy min(-1), over 90% of CaLS was mineralized to CO(2), H(2)O and sulfates within 3-d irradiation. The degradation of CaLS with the i... |
|
|
Contact allergy to calcium lignosulfonate.
Contact Dermatitis 6(5) , 354-5, (1980)
|
|
|
Calcium lignosulfonate adsorption and desorption on Berea sandstone
J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 279(1) , 36-45, (2004) This paper describes adsorption and desorption studies carried out with calcium lignosulfonate (CLS) on Berea sandstone. Circulation experiments were performed to determine CLS adsorption isotherms and the effects of CLS concentration, temperature, salinity, ... |
|
|
Methane hydrates with a high capacity and a high formation rate promoted by biosurfactants.
Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 48(95) , 11638-40, (2012) Lignosulfonates, which are byproducts of the pulp and paper industry, can be used as promoters for the formation of methane hydrates with a high capacity up to 170 v/v and a high formation rate. |