PD 151,242
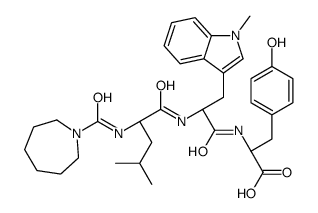
PD 151,242 structure
|
Common Name | PD 151,242 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 155561-67-4 | Molecular Weight | 619.75100 | |
| Density | 1.28g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 976.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C34H45N5O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 544.5ºC | |
|
A simple one-pot multicomponent synthesis of an octahedral nanocontainer molecule.
Nat. Protoc. 2 , 1288-96, (2007) A nearly quantitative 18-component synthesis of a nanocontainer, which is built up from six bowl-shaped cavitands that are connected together with 12 -CH=N-CH2CH2-N=CH- linkers, and its subsequent reduction are described. This nanocontainer has an estimated c... |
|
|
Endothelin-1[1-31], acting as an ETA-receptor selective agonist, stimulates proliferation of cultured rat zona glomerulosa cells.
FEBS Lett. 487(2) , 194-8, (2000) Endothelin-1 (ET-1)[1-31] is a novel hypertensive peptide that mimics many of the vascular effects of the classic 21 amino acid peptide ET-1[1-21]. However, at variance with ET-1[1-21] that enhances aldosterone secretion from cultured rat zona glomerulosa (ZG... |
|
|
Comparison of endothelin-A and endothelin-B receptor distribution visualized by radioligand binding versus immunocytochemical localization using subtype selective antisera.
J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 44 Suppl 1 , S224-6, (2004) Molecular studies have predicted the existence in human tissue of splice variants and modifications to the amino acid sequence of endothelin receptors that may modulate function. Endothelin-A (ETA) receptors were visualized by ligand binding and autoradiograp... |
|
|
Transient hypoxia/hypoglycemia upregulates endothelin B receptors in cultured rat astrocytes.
Glia 31(1) , 91-4, (2000) Endothelins are potent vasoactive peptides that bind to their specific receptors, playing an important role in the CNS under physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Astrocytes, which have been shown to express these receptors, also have a considerabl... |
|
|
Endothelin-1 binding to endothelin receptors in the rat anterior pituitary gland: possible formation of an ETA-ETB receptor heterodimer.
Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 22(2) , 207-26, (2002) 1. Interaction in the recognition of endothelin-1 (ET-1), a typical bivalent ET receptor-ligand, between ETA and ETB receptors was investigated in the rat anterior pituitary gland, using our quantitative receptor autoradiographic method with tissue sections p... |
|
|
Characterization of endothelin receptors in human brain cortex, gliomas, and meningiomas.
J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 26 Suppl 3 , S408-11, (1995) We have characterized the endothelin (ET) receptor subtypes present within normal human cerebral cortex (CC), glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), and meningiomas (MGs), using two subtype-selective radioligands, [125I]-PD151242 (ETA) and [125I]-BQ3020 (ETB). For sa... |
|
|
Relative contribution of endothelin A and endothelin B receptors to vasoconstriction in small arteries from human heart and brain.
J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 31 Suppl 1 , S74-6, (1998) Endothelin (ET) has been implicated in cardiovascular disorders such as stroke and myocardial ischemia. Given the important role of the resistance vasculature in the control of blood flow, we investigated the ET receptors that mediate vasoconstriction in huma... |
|
|
Stobadine is a potent modulator of endogenous endothelin-1 in human fibroblasts.
Life Sci. 65(18-19) , 1939-41, (1999) Binding of endothelin (ET) peptides to their respective receptors with resulting proliferation of vascular smooth muscle has been implicated in the pathogenesis of arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis. Recently it was hypothesized that endothelin- (ET-1)... |
|
|
Coronary and femoral arterial contraction with high glucose, insulin, and glucose-insulin-potassium solution: effects of hypoxia.
Heart Vessels 16(2) , 57-63, (2002) We studied whether the contractile responses to potassium chloride (KCI) of rat coronary and femoral arteries differ when perfused with solutions containing varying concentrations of metabolic substrates (glucose, oxygen, insulin) and whether these difference... |
|
|
Endothelin receptors in human coronary arteries.
Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 15(5) , 136-7, (1994)
|