AUDA
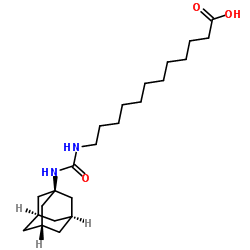
AUDA structure
|
Common Name | AUDA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 479413-70-2 | Molecular Weight | 392.575 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 592.7±19.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H40N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 312.3±21.5 °C | |
|
Intimal smooth muscle cells are a source but not a sensor of anti-inflammatory CYP450 derived oxylipins.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 463 , 774-80, (2015) Vascular pathologies are associated with changes in the presence and expression of morphologically distinct vascular smooth muscle cells. In particular, in complex human vascular lesions and models of disease in pigs and rodents, an intimal smooth muscle cell... |
|
|
Alkylphloroglucinol derivatives and triterpenoids with soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity from Callistemon citrinus.
Fitoterapia 109 , 39-44, (2016) Phytochemical analysis of the leaves and stems of Callistemon citrinus (Curtis) Skeels led to the isolation of two new alkylphloroglucinols, gallomyrtucommulone E and F (1 and 2), along with four other known alkylphloroglucinol derivatives, gallomyrtucommulon... |
|
|
Therapeutic effects of the soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitor AUDA on atherosclerotic diseases.
Pharmazie 70(1) , 24-8, (2015) In this study, we aimed to detect the effects of the soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitor 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid (AUDA) on atherosclerotic diseases and to explore its mechanism. The atherosclerosis animal model was constructed by Ap... |
|
|
Role of phosphatase activity of soluble epoxide hydrolase in regulating simvastatin-activated endothelial nitric oxide synthase.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13524, (2015) Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) has C-terminal epoxide hydrolase and N-terminal lipid phosphatase activity. Its hydrolase activity is associated with endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) dysfunction. However, little is known about the role of sEH phosphat... |
|
|
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition and gene deletion are protective against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 295(5) , H2128-34, (2008) Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) metabolizes epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) to dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids. EETs are formed from arachidonic acid during myocardial ischemia and play a protective role against ischemic cell death. Deletion of sEH has been sh... |
|
|
Soluble epoxide inhibition is protective against cerebral ischemia via vascular and neural protection.
Am. J. Pathol. 174 , 2086-95, (2009) Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase (SEH), the enzyme responsible for degradation of vasoactive epoxides, protects against cerebral ischemia in rats. However, the molecular and biological mechanisms that confer protection in normotension and hypertension ... |
|
|
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, AUDA, prevents early salt-sensitive hypertension.
Front. Biosci. 13 , 3480-7, (2008) In stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRSP) end-organ damage is markedly accelerated by high-salt (HS) intake. Since epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) possess vasodepressor and natriuretic activities, we examined whether a soluble epoxide hydrolase... |
|
|
Soluble epoxide hydrolase activity determines the severity of ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney.
PLoS ONE 7 , e37075, (2012) Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in endothelial cells determines the plasma concentrations of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which may act as vasoactive agents to control vascular tone. We hypothesized that the regulation of sEH activity may have a therapeu... |
|
|
The protective effect of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury is associated with PI3K/Akt pathway and ATP-sensitive potassium channels.
Neurochem. Res. 40(1) , 1-14, (2015) Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), the cytochrome P450 epoxygenase metabolite of arachidonic acid, have been demonstrated to have neuroprotective effect. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels are thought to be imp... |
|
|
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Deficiency or Inhibition Attenuates MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism.
Mol. Neurobiol. 52 , 187-95, (2015) Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibition has been demonstrated to have beneficial effects on various diseases, such as hypertension, diabetes, and brain ischemia. However, whether sEH inhibition has therapeutic potential in Parkinson's disease is still unkn... |