2-Amino-1-phenylethanone hydrochloride
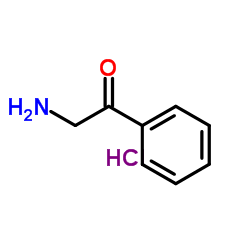
2-Amino-1-phenylethanone hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | 2-Amino-1-phenylethanone hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5468-37-1 | Molecular Weight | 171.624 | |
| Density | 1.084g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 247.3ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10ClNO | Melting Point | 194 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 103.4ºC | |
|
[Anorexigenic activity of various derivatives of alpha-aminoacetophenone].
Arch. Farmacol. Toxicol. 5(3) , 165-8, (1979)
|
|
|
Determination of cathinone, cathine and norephedrine in hair of Yemenite khat chewers.
Forensic Sci. Int. 133(1-2) , 39-46, (2003) A sensitive and reproducible method for the quantitative determination of cathinone (CTN), norpseudoephedrine (NPE, cathine) and norephedrine (NE) from hair was developed. The compounds were extracted for 4 hours with phosphate buffer pH 2.0, followed by a st... |
|
|
Mechanism-based inactivation of dopamine beta-monooxygenase by beta-chlorophenethylamine.
J. Biol. Chem. 259(12) , 7772-9, (1984) Functionalization of the beta-carbon of phenethylamines has been shown to produce a new class of substrate/inhibitor of dopamine beta-monooxygenase. Whereas both beta-hydroxy- and beta- chlorophenethylamine are converted to alpha-aminoacetophenone at comparab... |
|
|
Dopamine beta-hydroxylase: activity and inhibition in the presence of beta-substituted phenethylamines.
Biochemistry 21(1) , 67-75, (1982)
|
|
|
Use of isotope effects to characterize intermediates in mechanism-based inactivation of dopamine beta-monooxygenase by beta-chlorophenethylamine.
J. Biol. Chem. 265(10) , 5640-7, (1990) A mechanism for beta-chlorophenethylamine inhibition of dopamine beta-monooxygenase has been postulated in which bound alpha-aminoacetophenone is generated followed by an intramolecular redox reaction to yield a ketone-derived radical cation as the inhibitory... |
|
|
New entry of coupling reaction of phenacylamine derivatives with silylstannane.
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 50(3) , 441-3, (2002) The new coupling reaction of phenacylamines with silylstannane and lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) is reported. The treatment of a phenacylamine iodide 1 with (trimethylsilyl)tributylstannane (Me3SiSnBu3) and cesium fluoride (CsF) gave a dimerization product 2... |
|
|
Identification of small molecules rescuing fragile X syndrome phenotypes in Drosophila.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 4 , 256-63, (2008) Fragile X syndrome is caused by the functional loss of the fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene. Deletion of the FMR1 ortholog in Drosophila melanogaster (Fmr1) recapitulates many phenotypes associated with fragile X syndrome. We have discovered that Fm... |