Rubrene
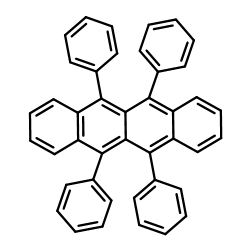
Rubrene structure
|
Common Name | Rubrene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 517-51-1 | Molecular Weight | 532.672 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 649.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C42H28 | Melting Point | >315 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 351.6±24.2 °C | |
|
Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of 9,10-diphenylanthracene, rubrene, and anthracene in fluorinated aromatic solvents.
J. Phys. Chem. A 112(37) , 8529-33, (2008) The electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) of 9,10-diphenylanthracene (DPA), rubrene, and anthracene has been studied in fluorinated aromatic solvents. Mixed annihilation ECL between aromatic luminophores and quinones was observed in solvent systems contain... |
|
|
Pure white organic light-emitting diode with lifetime approaching the longevity of yellow emitter.
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8th ed., 3 , 3134-3139, (2011) A high-efficiency pure white organic light-emitting diode was fabricated with lifetime approaching that of the low-excitation-energy (yellow) emitter containing counterpart, or six times that of the deep-blue counterpart. The white device was composed of two ... |
|
|
Chemiluminescent PEG-PCL micelles for imaging hydrogen peroxide.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 89(3) , 561-6, (2009) Hydrogen peroxide is one of the fundamental molecules of biology, regulating key cell signaling pathways and the development of numerous inflammatory diseases. There is therefore great interest in developing contrast agents that can detect hydrogen peroxide i... |
|
|
Induced crystallization of rubrene in thin-film transistors.
Adv. Mater. 22(30) , 3242-6, (2010)
|
|
|
Does bimolecular charge recombination in highly exergonic electron transfer afford the triplet excited state or the ground state of a photosensitizer?
J. Phys. Chem. A 112(4) , 635-42, (2008) The investigations were made on photoinduced electron transfer (ET) from the singlet excited state of rubrene (1RU*) to p-benzoquinone derivatives (duroquinone, 2,5-dimethyl-p-benzoquinone, p-benzoquinone, 2,5-dichloro-p-benzoquinone, and p-chloranil) in benz... |
|
|
Bias stress effect in "air-gap" organic field-effect transistors.
Adv. Mater. 24(20) , 2679-84, (2012) The origin of the bias stress effect related only to semiconductor properties is investigated in "air-gap" organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) in the absence of a material gate dielectric. The effect becomes stronger as the density of trap states in the ... |
|
|
The origin of a 650 nm photoluminescence band in rubrene.
Adv. Mater. 23(45) , 5370-5, (2011) Commonly observed variations in photoluminescence (PL) spectra of crystalline organic semiconductors, including the appearance or enhancement of certain PL bands, are shown to originate from a small amount of structural disorder (e.g., amorphous inclusions em... |
|
|
Magnetoresistance in an all-organic-based spin valve.
Adv. Mater. 23(30) , 3382-6, (2011)
|
|
|
Charge transport in organic crystals: role of disorder and topological connectivity.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(33) , 11702-8, (2010) We analyze the relationship among the molecular structure, morphology, percolation network, and charge carrier mobility in four organic crystals: rubrene, indolo[2,3-b]carbazole with CH(3) side chains, and benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bis[b]benzothiophene derivatives w... |
|
|
Charge reorganization energy and small polaron binding energy of rubrene thin films by ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy.
Adv. Mater. 24(7) , 901-5, (2012) The hole–phonon coupling of a rubrene monolayer on graphite is measured by means of angle resolved ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy. Thus, the charge reorganization energy λ and the small polaron binding energy is determined, which allows insight into t... |