Maltose monohydrate
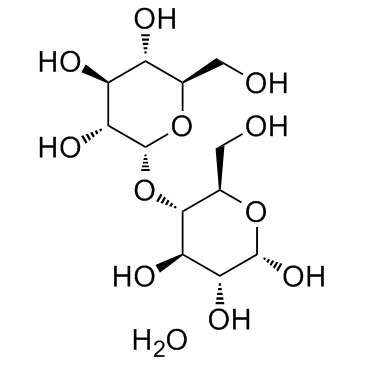
Maltose monohydrate structure
|
Common Name | Maltose monohydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6363-53-7 | Molecular Weight | 360.312 | |
| Density | 1.768g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 667.931ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H24O12 | Melting Point | 119-121 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 357.752ºC | |
|
Susceptibility of glutinous rice starch to digestive enzymes.
Carbohydr. Polym. 128 , 154-62, (2015) To understand the susceptibility of glutinous rice starch to digestive enzymes and its potential impact on glycemic response, enzyme kinetics and in vitro digestibility of the native and gelatinized starches were investigated. The results showed that the Km v... |
|
|
Analysis of underivatized cellodextrin oligosaccharides by capillary electrophoresis with direct photochemically induced UV-detection.
Electrophoresis 36 , 1555-63, (2015) This work focuses on the development of a CE method allowing, for the first time, the simultaneous separation of the underivatized first seven cellodextrin oligomers (glucose, cellobiose, cellotriose, cellotetraose, cellopentaose, cellohexaose, and cellohepta... |
|
|
Kinetics and equilibria of the chromatographic separation of maltose and trehalose.
J. Sep. Sci. 38 , 2229-37, (2015) Trehalose, a nonreducing disaccharide, has been extensively applied to food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical goods. The resultant solution of trehalose prepared by enzymatic methods includes high amounts of maltose. However, it is quite difficult to separate ma... |
|
|
GC-MS Method for the Quantitation of Carbohydrate Intermediates in Glycation Systems.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 5911-9, (2015) Glycation is a ubiquitous nonenzymatic reaction of carbonyl compounds with amino groups of peptides and proteins, resulting in the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) and thereby affecting the properties and quality of thermally processed food... |
|
|
Contact-dependent growth inhibition causes reversible metabolic downregulation in Escherichia coli.
J. Bacteriol. 191(6) , 1777-86, (2009) Contact-dependent growth inhibition (CDI) is a mechanism identified in Escherichia coli by which bacteria expressing two-partner secretion proteins encoded by cdiA and cdiB bind to BamA in the outer membranes of target cells and inhibit their growth. A third ... |
|
|
Separation behaviour of some isomeric organic compounds on sugars, sugar alcohols and their mixed phases by gas-liquid chromatography. Ono, A.
J. Chromatogr. A. 197 , 251, (1980)
|