7-Methylguanosine 5'-diphosphate sodium
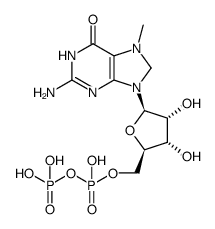
7-Methylguanosine 5'-diphosphate sodium structure
|
Common Name | 7-Methylguanosine 5'-diphosphate sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104809-16-7 | Molecular Weight | 459.24300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H19N5O11P2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Elimination of cap structures generated by mRNA decay involves the new scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme Aph1/FHIT together with DcpS.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43(1) , 482-92, (2015) Eukaryotic 5' mRNA cap structures participate to the post-transcriptional control of gene expression before being released by the two main mRNA decay pathways. In the 3'-5' pathway, the exosome generates free cap dinucleotides (m7GpppN) or capped oligoribonuc... |
|
|
Loss of the scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme DCPS causes syndromic intellectual disability with neuromuscular defects.
Hum. Mol. Genet. 24(11) , 3163-71, (2015) mRNA decay is an essential and active process that allows cells to continuously adapt gene expression to internal and environmental cues. There are two mRNA degradation pathways: 3' to 5' and 5' to 3'. The DCPS protein is the scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme w... |
|
|
7-methylguanosine diphosphate (m(7)GDP) is not hydrolyzed but strongly bound by decapping scavenger (DcpS) enzymes and potently inhibits their activity.
Biochemistry 51(40) , 8003-13, (2012) Decapping scavenger (DcpS) enzymes catalyze the cleavage of a residual cap structure following 3' → 5' mRNA decay. Some previous studies suggested that both m(7)GpppG and m(7)GDP were substrates for DcpS hydrolysis. Herein, we show that mononucleoside diphosp... |
|
|
Characterization of a second vaccinia virus mRNA-decapping enzyme conserved in poxviruses.
J. Virol. 81(23) , 12973-8, (2007) Vaccinia virus (VACV) encodes enzymes that cap the 5' end of viral mRNAs, which enhances their stability and translation. Nevertheless, recent studies demonstrated that the VACV D10 protein (VACV-WR_115) decaps mRNA, an enzymatic activity not previously shown... |
|
|
Internal and overall motions of the translation factor eIF4E: cap binding and insertion in a CHAPS detergent micelle.
J. Biomol. NMR 12(1) , 73-88, (1998) The mRNA cap-binding protein eIF4E is the limiting factor in the eIF4F translation initiation complex, which mediates the binding of the 40S ribosome to the mRNA. 15N relaxation studies have been used to characterize the backbone dynamics of deuterated eIF4E ... |
|
|
A procedure for analysis of stopped-flow transients for protein-ligand association.
J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 51(2) , 179-93, (2002) A method for extracting kinetic and optical parameters from progress curves for protein-ligand association, obtained by stopped-flow experiments, is described. The method is limited to one-step and two-step association kinetics, but it allows concentration of... |
|
|
Solution-based approach to study binding to the eIF4E cap-binding site using CD spectroscopy.
Anal. Biochem. 434(1) , 166-71, (2013) The eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) is the key component of the translational initiation complex that recruits mRNA by binding to a unique "cap" structure located at the 5' end of the mRNA. Overexpression of eIF4E has been implicated in the developmen... |
|
|
DcpS can act in the 5'-3' mRNA decay pathway in addition to the 3'-5' pathway.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100 , 12081-12086, (2003) Eukaryotic mRNA degradation proceeds through two main pathways, both involving mRNA cap breakdown. In the 3'-5' mRNA decay pathway, mRNA body degradation generates free m7GpppN that is hydrolyzed by DcpS generating m7GMP. In the 5'-3' pathway, the recently id... |
|
|
Chemical synthesis and binding activity of the trypanosomatid cap-4 structure.
RNA 10 , 1469-1478, (2004) Leishmania and other trypanosomatids are early eukaryotes that possess unusual molecular features, including polycistronic transcription and trans-splicing of pre-mRNAs. The spliced leader RNA (SL RNA) is joined to the 5' end of all mRNAs, thus donating a 5' ... |
|
|
Backbone resonance assignment of human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) in complex with 7-methylguanosine diphosphate (m7GDP) and a 17-amino acid peptide derived from human eIF4GII.
J. Biomol. NMR 27 , 279-280, (2003)
|