HEPPS
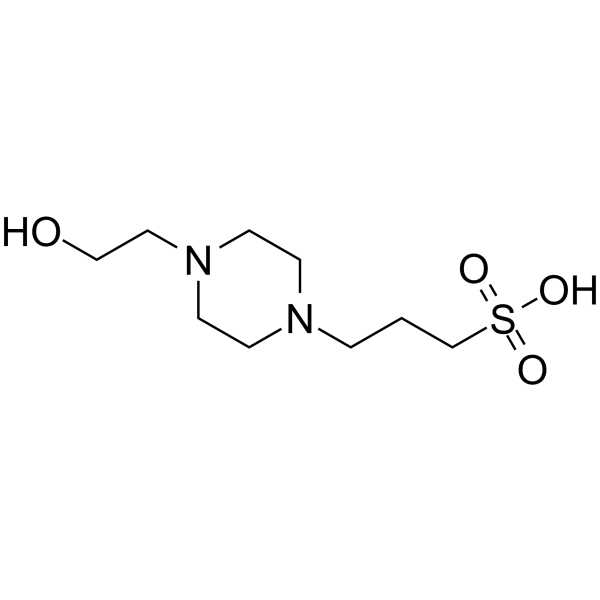
HEPPS structure
|
Common Name | HEPPS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16052-06-5 | Molecular Weight | 252.331 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H20N2O4S | Melting Point | 237-239 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Comparison of MDCK-MDR1 and Caco-2 cell based permeability assays for anti-malarial drug screening and drug investigations.
J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 70(2) , 188-94, (2014) Malaria is a major health concern and affects over 300million people a year. Accordingly, there is an urgent need for new efficacious anti-malarial drugs. A major challenge in developing new anti-malarial drugs is to design active molecules that have preferab... |
|
|
Heat Shock Protein 90 Associates with the Per-Arnt-Sim Domain of Heme-free Soluble Guanylate Cyclase: IMplications for Enzyme Maturation.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 21615-28, (2015) Heat shock protein 90 (hsp90) drives heme insertion into the β1 subunit of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) β1, which enables it to associate with a partner sGCα1 subunit and mature into a nitric oxide (NO)-responsive active form. We utilized fluorescence pola... |
|
|
EPPS rescues hippocampus-dependent cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice by disaggregation of amyloid-β oligomers and plaques.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 8997, (2015) Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the transition of amyloid-β (Aβ) monomers into toxic oligomers and plaques. Given that Aβ abnormality typically precedes the development of clinical symptoms, an agent capable of disaggregating existing Aβ aggregat... |
|
|
The infiltration and functional regulation of eosinophils induced by TSLP promote the proliferation of cervical cancer cell.
Cancer Lett. 364 , 106-17, (2015) Cervical cancer is often associated with eosinophil (EOS) infiltration, but the source and the role of EOS are still largely unknown. Our previous work has established that thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) can stimulate the growth of cervical cancer cell i... |
|
|
GPR4 decreases B16F10 melanoma cell spreading and regulates focal adhesion dynamics through the G13/Rho signaling pathway.
Exp. Cell Res. 334 , 100-13, (2015) The effect of acidosis, a biochemical hallmark of the tumor microenvironment, on cancer progression and metastasis is complex. Both pro- and anti-tumorigenic effects of acidosis have been reported and the acidic microenvironment has been exploited for specifi... |
|
|
P.Gill, J.G. Sutton
Electrophoresis 6 , 23, (1985)
|