ACES
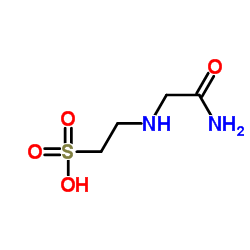
ACES structure
|
Common Name | ACES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7365-82-4 | Molecular Weight | 182.198 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10N2O4S | Melting Point | >220 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Xanthine derivatives quantification in serum by capillary zone electrophoresis.
J. Chromatogr. Sci. 52(9) , 1121-6, (2014) A capillary electrophoresis method was developed to quantify caffeine and theophylline, xanthine derivatives with bronchodilator activity. Buffer concentration, pH and applied voltage were optimized using a central composite design-face centred. Separation co... |
|
|
Characterization of asparagine 330 deamidation in an Fc-fragment of IgG1 using cation exchange chromatography and peptide mapping.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 965 , 65-71, (2014) Deamidation is one of the most common degradation pathways for proteins and frequently occurs at "hot spots" with Asn-Gly, Asn-Ser or Asn-Thr sequences. Occasionally, deamidation may occur at other motifs if the local protein structure can participate or assi... |
|
|
Phosphate modulates receptor sulfotyrosine recognition by the chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2).
Org. Biomol. Chem. 13(7) , 2162-9, (2015) Tyrosine sulfation is a widespread post-translational modification that mediates the interactions of secreted and membrane-associated proteins in such varied biological processes as peptide hormone action, adhesion, blood coagulation, complement activation an... |
|
|
Isolation and classification of a novel marine Bacteroidetes as Frondibacter aureus gen. nov., sp. nov.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107(2) , 321-8, (2015) A facultatively anaerobic, Gram-stain negative, golden-yellow pigmented, non-motile and rod-shaped bacterium, designated strain A5Q-67(T) was isolated from leaf litter collected at the mangrove estuary of Nakama River, Japan. Phylogenetic analysis based on th... |
|
|
Legionella dumoffii utilizes exogenous choline for phosphatidylcholine synthesis.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15(5) , 8256-79, (2014) Phosphatidycholine (PC) is the major membrane-forming phospholipid in eukaryotes but it has been found in only a limited number of prokaryotes. Bacteria synthesize PC via the phospholipid N-methylation pathway (Pmt) or via the phosphatidylcholine synthase pat... |
|
|
Phylogenetic and taxonomic analysis of Neptunitalea chrysea gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the phylum Bacteroidetes isolated from seawater by using an in situ cultivation technique.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108 , 537-44, (2015) A novel pale-yellow coloured bacterial strain, designated AM327(T), was isolated by using an in situ cultivation technique from seawater from the coastal zone around a shipyard located in Otsuchi Bay, Japan. The strain was found to be facultatively anaerobic,... |
|
|
Recognition of the DNA minor groove by thiazotropsin analogues.
ChemBioChem. 15(13) , 1978-90, (2014) Solution-phase self-association characteristics and DNA molecular-recognition properties are reported for three close analogues of minor-groove-binding ligands from the thiazotropsin class of lexitropsin molecules; they incorporate isopropyl thiazole as a lip... |
|
|
DNA sequencing using polymerase substrate-binding kinetics.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 5936, (2015) Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has transformed genomic research by decreasing the cost of sequencing. However, whole-genome sequencing is still costly and complex for diagnostics purposes. In the clinical space, targeted sequencing has the advantage of allo... |
|
|
Free metal ion depletion by "Good's" buffers. II. N-(2-acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid (ACESH): complexes with calcium(II), magnesium(II), manganese(II), cobalt(II), zinc(II), nickel(II), and copper(II).
Anal. Biochem. 103(2) , 214-21, (1980)
|
|
|
N-[(carbamoylmethyl)amino]ethanesulfonic acid improves phenotyping of alpha 1-antitrypsin by isoelectric focusing on agarose gel.
Clin. Chem. 31 , 1384, (1985) The hereditary deficiency variants of alpha 1-antitrypsin that are associated with diseases such as emphysema are usually identified by use of isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gels. Agarose is a simpler, faster, safer, and more reliable medium for this,... |