calcium carbonate
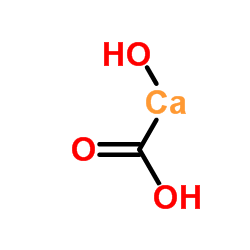
calcium carbonate structure
|
Common Name | calcium carbonate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 471-34-1 | Molecular Weight | 100.09 | |
| Density | 2.93 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 800 °C | |
| Molecular Formula | CaCO3 | Melting Point | 825 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 197ºC | |
|
Development of a novel calcium phosphate cement composed mainly of calcium sodium phosphate with high osteoconductivity.
J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 25(6) , 1505-17, (2014) Two novel calcium phosphate cements (CPC) have been developed using calcium sodium phosphate (CSP) as the main ingredient. The first of these cements, labeled CAC, contained CSP, α-tricalcium phosphate (TCP), and anhydrous citric acid, whereas the second, lab... |
|
|
Coculture of peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells on strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate scaffolds to generate vascularized engineered bone.
Tissue Eng. Part A 21(5-6) , 948-59, (2015) Vascularization of engineered bone tissue is critical for ensuring its survival after implantation and it is the primary factor limiting its clinical use. A promising approach is to prevascularize bone grafts in vitro using endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) ... |
|
|
Characterization of the Dual Subcellular Localization of Lilium LsGRP1, a Plant Class II Glycine-Rich Protein.
Phytopathology 104(10) , 1012-20, (2014) The defense-related gene LsGRP1 exhibits an increased level of expression in Lilium spp. after being infected by Botrytis elliptica, the fungal pathogen of lily leaf blight. In this study, the expression profile of the LsGRP1 protein (a plant class II glycine... |
|
|
Factors affecting lead release in sodium silicate-treated partial lead service line replacements.
J. Environ. Sci. Health. A. Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 50 , 922-30, (2015) Water quality parameters affecting sodium silicate performance in partial lead service line replacements were examined using a fractional factorial experimental design and static pipe systems. An external copper wire was used to create a galvanic connection b... |
|
|
Remineralization efficacy of a toothpaste containing 8% arginine and calcium carbonate on enamel surface.
Am. J. Dent. 26(5) , 291-7, (2013) To investigate the remineralization efficacy of different types of toothpastes on initial enamel lesions in vitro.Artificial initial lesions were created on 150 enamel discs from freshly extracted bovine incisors. These enamel discs were divided into five gro... |
|
|
Effects of UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic composition of leaves and berries of Vitis vinifera cv. Graciano.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(2) , 409-16, (2014) Ultraviolet (UV) radiation induces adaptive responses that can be used for plant production improvement. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of solar UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic compounds of leaves and berry skins of Vitis vinifera ... |
|
|
Zebrafish genome instability after exposure to model genotoxicants.
Ecotoxicology 24(4) , 887-902, (2015) Sublethal exposure to environmental genotoxicants may impact genome integrity in affected organisms. It is therefore necessary to develop tools to measure the extent and longevity of genotoxicant-induced DNA damage, and choose appropriate model organisms for ... |
|
|
Bacteriophages of wastewater foaming-associated filamentous Gordonia reduce host levels in raw activated sludge.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13754, (2015) Filamentous bacteria are a normal and necessary component of the activated sludge wastewater treatment process, but the overgrowth of filamentous bacteria results in foaming and bulking associated disruptions. Bacteriophages, or phages, were investigated for ... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of oxalotrophic bacteria from tropical soils.
Arch. Microbiol. 197(1) , 65-77, (2015) The oxalate-carbonate pathway (OCP) is a biogeochemical set of reactions that involves the conversion of atmospheric CO2 fixed by plants into biomass and, after the biological recycling of calcium oxalate by fungi and bacteria, into calcium carbonate in terre... |
|
|
Late Miocene threshold response of marine algae to carbon dioxide limitation.
Nature 500(7464) , 558-62, (2013) Coccolithophores are marine algae that use carbon for calcification and photosynthesis. The long-term adaptation of these and other marine algae to decreasing carbon dioxide levels during the Cenozoic era has resulted in modern algae capable of actively enhan... |