Etofenamate
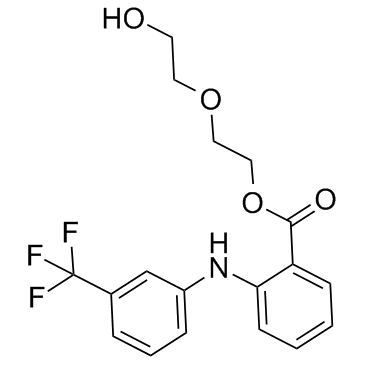
Etofenamate structure
|
Common Name | Etofenamate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 30544-47-9 | Molecular Weight | 369.335 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 451.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H18F3NO4 | Melting Point | 25°C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 226.6±28.7 °C | |
|
Adverse reaction of topical etofenamate: petechial eruption.
West Indian Med. J. 61(7) , 767-9, (2012) Etofenamate is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Clinical findings caused by etofenamate are uncommon. Allergic contact dermatitis is the most common cutaneous reaction reported. But petechial eruption due to etofenamate had not been reported ye... |
|
|
Turpentine sensitization in a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory solution user.
Dermatitis 23(4) , 182-3, (2012)
|
|
|
Assessing the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a full-scale activated sludge plant.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 19(5) , 1818-27, (2012) This study aimed to investigate the removal mechanisms of pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) and musks in a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Biological removal and adsorption in the activated sludge tank as well as the effect of UV radiation used for d... |
|
|
[Plasma- and tissue concentrations following intramuscular administration of etofenamat. Pharmacokinetics of etofenamat and flufenamic acid in plasma, synovium, and tissues of patients with chronic polyarthritis after administration of an oily solution of etofenamat].
Arzneimittelforschung 42(12) , 1487-91, (1992) Studies on Plasma and Tissue Concentrations of Etofenamate following Intramuscular Application/Pharmacokinetics of etofenamate and flutenamic acid in plasma, synovia and tissues of patients with chronic polyarthritis after application of oily etofenamat solut... |
|
|
Effects of some pharmacological agents on the survival of unipedicled venous flaps: an experimental study.
Microsurgery 21(8) , 350-6, (2001) Clinical and experimental studies have been conducted to improve the survival of venous flaps. As a result of these studies, although various survival mechanisms were raised, none obtained satisfactory information. Venous stasis, and the resultant venous thro... |
|
|
Influence of preemptive analgesia on pulmonary function and complications for laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Dig. Dis. Sci. 54(12) , 2742-7, (2009) Pain and diaphragmatic dysfunction are the major reasons for postoperative pulmonary complications after upper abdominal surgery. Preoperative administration of analgesics helps to reduce and prevent pain. The objective of this study was first to research the... |
|
|
Etofenamate levels in human serum and synovial fluid following iontophoresis.
Arzneimittelforschung 51(6) , 489-92, (2001) The absorption of etofenamate (CAS 30544-47-9, Rheumon gel) by iontophoresis in 11 patients with low back pain and in 13 patients with synovitis of the knee was evaluated. During the 5-day treatment period, the test gel in a quantity corresponding to 100 mg e... |
|
|
Comparative study of etofenamate and fentanyl for outpatient extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy.
Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 35(6) , 502-4, (2001) This study aimed to compare the clinical efficacy and safety of etofenamate (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) and fentanyl (an opioid analgesic) for outpatient extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL).60 non-premedicated patients underwent ESWL for... |
|
|
Action spectrum for etofenamate photoallergic contact dermatitis.
Contact Dermatitis 65(2) , 117-8, (2011)
|
|
|
Etofenamate associated with Lyell syndrome: a case report.
Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 48(5) , 471-2, (2010) Toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell syndrome) is a rare, acute, and potentially life-threatening mucocutaneous disease that is most often triggered by drugs. This is the first case of toxic epidermal necrolysis because of treatment with etofenamate of which we ... |