Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser
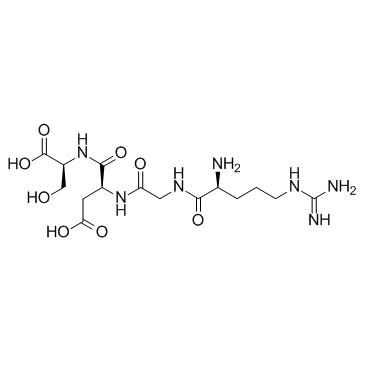
Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser structure
|
Common Name | Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 91037-65-9 | Molecular Weight | 433.41700 | |
| Density | 1.65g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H27N7O8 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Oligodendrocytes Are Targets of HIV-1 Tat: NMDA and AMPA Receptor-Mediated Effects on Survival and Development.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 11384-98, (2015) Myelin pallor in HIV(+) individuals can occur very early during the disease process. While myelin damage might partly originate from HIV-induced vascular changes, the timing suggests that myelin and/or oligodendrocytes (OLs) may be directly affected. Histolog... |
|
|
Emulating native periosteum cell population and subsequent paracrine factor production to promote tissue engineered periosteum-mediated allograft healing.
Biomaterials 52 , 426-40, (2015) Emulating autograft healing within the context of decellularized bone allografts has immediate clinical applications in the treatment of critical-sized bone defects. The periosteum, a thin, osteogenic tissue that surrounds bone, houses a heterogenous populati... |
|
|
Cross-talk between transforming growth factor-β₁ and muscarinic M₂ receptors augments airway smooth muscle proliferation.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 49(1) , 18-27, (2013) Transforming growth factor-β₁ (TGF-β₁) is a central mediator in tissue remodeling processes, including fibrosis and airway smooth muscle (ASM) hyperplasia, as observed in asthma. The mechanisms underlying this response, however, remain unclear because TGF-β₁ ... |
|
|
Improved Angiogenesis in Response to Localized Delivery of Macrophage-Recruiting Molecules.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0131643, (2015) Successful engineering of complex organs requires improved methods to promote rapid and stable vascularization of artificial tissue scaffolds. Toward this goal, tissue engineering strategies utilize the release of pro-angiogenic growth factors, alone or in co... |
|
|
Agonism of Wnt-β-catenin signalling promotes mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) expansion.
J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9 , E13-26, (2015) Promoting mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) proliferation has numerous applications in stem cell therapies, particularly in the area of regenerative medicine. In order for cell-based regenerative approaches to be realized, MSC proliferation must be achieved in a co... |
|
|
The roles of integrins in function of human neutrophils after their migration through endothelium into interstitial matrix.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0118593, (2015) We investigated the changes in neutrophil phenotype and function after transendothelial migration, and the roles played by integrin receptors in their behaviour. Neutrophils were tracked microscopically as they migrated through endothelial cells into collagen... |
|
|
RGDS-fuctionalized alginates improve the survival rate of encapsulated embryonic stem cells during cryopreservation.
Cryo. Letters 32(5) , 389-401, (2011) Cryopreservation of stem cells, especially embryonic stem cells, is problematic because of low post-thaw cell survival rates and spontaneous differentiation following recovery. In this investigation, mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) were encapsulated in arg... |
|
|
Multifactorial optimization of endothelial cell growth using modular synthetic extracellular matrices.
Integr. Biol. (Camb.) 3(3) , 185-96, (2011) Extracellular matrices (ECMs) are complex materials, containing at least dozens of different macromolecules that are assembled together, thus complicating their optimization towards applications in 3D cell culture or tissue engineering. The natural complexity... |
|
|
Dense surface functionalization using peptides that recognize differences in organized structures of self-assembling nanomaterials.
Mol. Biosyst. 8(4) , 1264-74, (2012) We obtained novel peptides that selectively bind to self-assembling peptide nanomaterials from a random peptide library displayed on phages. Affinity-dependent peptide screening gave phage clones displaying peptides with selective affinities against two kinds... |
|
|
Density gradient multilayered polymerization (DGMP): a novel technique for creating multi-compartment, customizable scaffolds for tissue engineering.
J. Vis. Exp. (72) , doi:10.3791/50018, (2013) Complex tissue culture matrices, in which types and concentrations of biological stimuli (e.g. growth factors, inhibitors, or small molecules) or matrix structure (e.g. composition, concentration, or stiffness of the matrix) vary over space, would enable a wi... |