Manumycin A
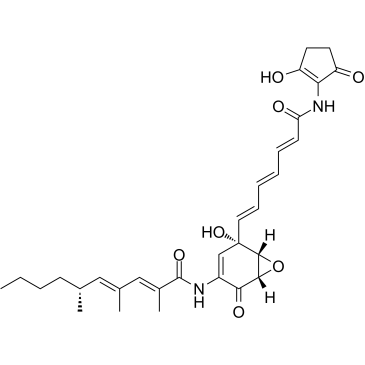
Manumycin A structure
|
Common Name | Manumycin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 52665-74-4 | Molecular Weight | 550.643 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 863.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H38N2O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 476.1±34.3 °C | |
|
Statins inhibit protein lipidation and induce the unfolded protein response in the non-sterol producing nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106(43) , 18285-90, (2009) Statins are compounds prescribed to lower blood cholesterol in millions of patients worldwide. They act by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the mevalonate pathway that leads to the synthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate, a precursor for ... |
|
|
[Effects of manumycin combined with methoxyamine on apoptosis in myeloid leukemia U937 cells].
Chin. J. Cancer 27(8) , 835-9, (2008) Repair of DNA damage is important to cell survival. Our previous study showed DNA damage response induced by manumycin in cancer cells. We hypothesized that methoxyamine, an inhibitor of base-excision repair, can enhance the antineoplastic effect of manumycin... |
|
|
Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces murine fibrosarcoma L929 cell apoptosis and autophagy via blocking Ras-Raf and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways.
Biochimie 92(12) , 1934-8, (2010) Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin (PCL), a mannose/sialic acid-binding lectin, has been reported to display remarkable anti-proliferative and apoptosis-inducing activities toward a variety of cancer cells; however, the precise molecular mechanisms by which PCL ind... |
|
|
Plumbagin activates ERK1/2 and Akt via superoxide, Src and PI3-kinase in 3T3-L1 cells.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 638(1-3) , 21-8, (2010) Plumbagin, derived from the plant Plumbago zeylanica, has been shown to chronically activate ERK1/2 and inhibit Akt activity in cancer cells. However, the acute effects of plumbagin on ERK1/2 and Akt activities remain unknown. In this study, we examined the e... |
|
|
Farnesyltransferase inhibitors reduce Ras activation and ameliorate acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice.
Hepatology 50(5) , 1547-57, (2009) Hepatotoxicity due to overdose of the analgesic and antipyretic acetaminophen (APAP) is a major cause of liver failure in adults. To better understand the contributions of different signaling pathways, the expression and role of Ras activation was evaluated a... |
|
|
Genome-wide screen for modulation of hepatic apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) secretion.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(9) , 6386-96, (2013) Control of plasma cholesterol levels is a major therapeutic strategy for management of coronary artery disease (CAD). Although reducing LDL cholesterol (LDL-c) levels decreases morbidity and mortality, this therapeutic intervention only translates into a 25-4... |
|
|
Phosphorylation of histone H3 at Ser10: its role in cell transformation by v-Src.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 386(4) , 588-92, (2009) We found that transformation by v-src constitutively activated phosphorylation of histone H3 at Ser10 in a transformation-specific manner. While nontransforming mutant of v-src did not activate H3 phosphorylation, H3 phosphorylation in cells expressing temper... |
|
|
Reversal of age-dependent nuclear morphology by inhibition of prenylation does not affect lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Nucleus 1(6) , 499-505, (2010) Fibroblasts derived from Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) patients and dermal cells derived from healthy old humans in culture display age-dependent progressive changes in nuclear architecture due to accumulation of farnesylated lamin A. Treating h... |
|
|
Transcriptional regulation and increased production of asukamycin in engineered Streptomyces nodosus subsp. asukaensis strains.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 96(2) , 451-60, (2012) Asukamycin, a member of the manumycin family of antibiotics, exhibits strong antibacterial, antifungal, and antineoplastic activities. However, its production in the wild-type strain of Streptomyces nodosus subsp. asukaensis ATCC 29757 is relatively low. Rece... |
|
|
Autophagy induced by farnesyltransferase inhibitors in cancer cells.
Cancer Biol. Ther. 7(10) , 1679-84, (2008) The mechanisms of action of farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs) involve Rheb and the phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. mTOR in particular plays a key role in the regulation of autophagy. Collectively, the liter... |