Canthaxanthin
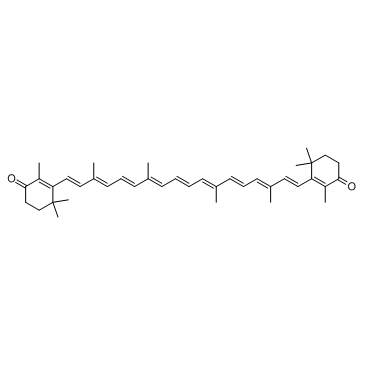
Canthaxanthin structure
|
Common Name | Canthaxanthin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 514-78-3 | Molecular Weight | 564.840 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 717.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C40H52O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 253.9±24.3 °C | |
|
Developing an emulsion model system containing canthaxanthin biosynthesized by Dietzia natronolimnaea HS-1.
Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 51(4) , 618-26, (2012) An acceptable strategy to incorporate canthaxanthin (CX) as a natural colorant into products is by means of oil-in-water emulsions. The used CX in this study was produced by bacterium Dietzia natronolimnaea HS-1 using a batch bioreactor system. A central comp... |
|
|
Influence of canthaxanthin on broiler breeder reproduction, chick quality, and performance.
Poult. Sci. 90(7) , 1516-22, (2011) To investigate the effect of canthaxanthin supplied via a maternal route on the production of both breeder hens and chickens, 270 Chinese Three-Yellow breeder hens were randomly divided into 2 groups consisting of 135 birds each (5 replicates of 27) for study... |
|
|
Determination of supplemental feeding needs for astaxanthin and canthaxanthin in salmonids by supramolecular solvent-based microextraction and liquid chromatography-UV/VIS spectroscopy.
Food Chem. 134(2) , 1244-9, (2012) Development of simple and rapid analytical methods for predicting supplemental feeding requirements in aquaculture is a need to reduce production costs. In this article, a supramolecular solvent (SUPRAS) made up of decanoic acid (DeA) assemblies was proposed ... |
|
|
Optimization of process parameters by response surface methodology and kinetic modeling for batch production of canthaxanthin by Dietzia maris NIT-D (accession number: HM151403).
Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 35(8) , 1375-88, (2012) Dietzia maris NIT-D, a canthaxanthin producer, was isolated during routine screening of pigment-producing bacteria. Response surface methodology was applied for statistical designing of process parameters for biomass and canthaxanthin production. The effects ... |
|
|
Carotenogenesis up-regulation in Scenedesmus sp. using a targeted metabolomics approach by liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(7) , 3004-13, (2011) Carotenoids have potent antioxidant activity as well as therapeutic value, and their formation has been seen to be induced in algae by stress, including high-salt culture conditions. A differential profiling of carotenoids was conducted using a targeted metab... |
|
|
Dietary values of astaxanthin and canthaxanthin in Penaeus monodon in the presence and absence of cholesterol supplementation: effect on growth, nutrient digestibility and tissue carotenoid composition.
Br. J. Nutr. 108(1) , 80-91, (2012) Penaeus monodon (mean initial wet weight 1·19 (SE 0·01) g) were fed seven diets in triplicate: a control diet (D1) without carotenoids; three diets formulated to supply 0·1 % astaxanthin alone (D2), 0·2 % astaxanthin alone (D3), and a combination of 0·1 % ast... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of a lycopene ε-cyclase gene of Chlorella (Chromochloris) zofingiensis. Regulation of the carotenogenic pathway by nitrogen and light.
Mar. Drugs 10(9) , 2069-88, (2012) The isolation and characterization of the lycopene ε-cyclase gene from the green microalga Chlorella (Chromochloris) zofingiensis (Czlcy-e) was performed. This gene is involved in the formation of the carotenoids α-carotene and lutein. Czlcy-e gene encoded a ... |
|
|
Synthesis of highly 13C enriched carotenoids: access to carotenoids enriched with 13C at any position and combination of positions.
Acta Biochim. Pol. 59(1) , 11-6, (2012) Carotenoids and their metabolites are essential factors for the maintenance of important life processes such as photosynthesis. Animals cannot synthesize carotenoids de novo, they must obtain them via their food. In order to make intensive animal husbandry po... |
|
|
Impact of dietary carotenoid and packaging during frozen storage on the quality of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed carotenoids.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 91(6) , 1075-82, (2011) The storage life of frozen salmonids is often limited primarily by oxidation and flesh discolouration due to carotenoid degradation. The objective of this research was to determine the carotenoid changes and therefore the muscle colour modifications during 6 ... |
|
|
Antioxidant and lipid peroxidation activities in rats fed with Aspergillus carbonarius carotenoid
Food Chem. Toxicol. 49(12) , 3098-103, (2011) Highlights ► Serum total and LDL-cholesterol levels were influenced by the dietary carotenoid. ► Intake of PSC beneficially affected the hepatic ascorbic content and lipid peroxides. ► Glutathione transferase and catalase activities are enhanced in PSC treate... |