Buprofezin
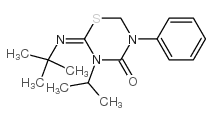
Buprofezin structure
|
Common Name | Buprofezin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69327-76-0 | Molecular Weight | 305.43800 | |
| Density | 1.18 | Boiling Point | 273°C (12 torr) | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H23N3OS | Melting Point | 104-106°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 176-178°C | |
|
Effect of repeated applications of buprofezin and acephate on soil cellulases, amylase, and invertase.
Environ. Monit. Assess. 186(10) , 6319-25, (2014) The impact of repeated applications of buprofezin and acephate, at concentrations ranging from 0.25 to 1.0 kg ha(-1), on activities of cellulases, amylase, and invertase in unamended and nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium (NPK) fertilizer-amended soil plant... |
|
|
Effects of pyriproxyfen and buprofezin on immature development and reproduction in the stable fly.
Med. Vet. Entomol. 26(4) , 379-85, (2012) The stable fly, Stomoxys calcitrans (L.) (Diptera: Muscidae), is one of the most significant biting flies that affect cattle. The use of traditional insecticides for stable fly control has only a limited success owing to the insect's unique feeding behaviours... |
|
|
Action threshold for applying insect growth regulators to tomato for management of irregular ripening caused by Bemisia argentifolii (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae).
J. Econ. Entomol. 95(2) , 372-6, (2002) The whitefly Bemisia argentifolii Bellows & Perring is a major pest of tomatoes, causing an irregular ripening disorder characterized externally by incomplete or inhibited reddening of fruit, especially in longitudinal sections, and internally by an increase ... |
|
|
Baseline susceptibility of Planococcus ficus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) from California to select insecticides.
J. Econ. Entomol. 105(4) , 1392-400, (2012) Between 2006 and 2008, 20 populations of Planococcus ficus (Signoret), from Coachella and San Joaquin Valleys of California were measured in the laboratory for susceptibility to buprofezin, chlorpyrifos, dimethoate, methomyl, and imidacloprid. Toxicity was as... |
|
|
Compatibility of the entomopathogenic fungus Lecanicillium muscarium and insecticides for eradication of sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci.
Mycopathologia 160(1) , 35-41, (2005) The compatibility of the entomopathogenic fungus Lecanicillium muscarium and chemical insecticides used to control the second instar stages of the sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci, was investigated. The effect on spore germination of direct exposure for 2... |
|
|
Ecotoxicological effects of buprofezin on fecundity, growth, development, and predation of the wolf spider Pirata piratoides (Schenkel).
Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 55(4) , 652-8, (2008) The toxicological effects of buprofezin, an insect growth regulator, on the fecundity, development, and pest control potential of the wolf spider Pirata piratoides (Schenkel) (Araneae: Lycosidae) were investigated in the laboratory. It was shown that buprofez... |
|
|
Isolation of a buprofezin co-metabolizing strain of Pseudomonas sp. DFS35-4 and identification of the buprofezin transformation pathway.
Biodegradation 22(6) , 1135-42, (2011) Buprofezin is a widely used insecticide that has caused environmental pollution in many areas. However, biodegradation of buprofezin by pure cultures has not been extensively studied, and the transformation pathway of buprofezin remains unclear. In this paper... |
|
|
Effect of pH on the persistence behavior of the insecticide buprofezin in water under laboratory conditions.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 72(2) , 307-11, (2004)
|
|
|
[Effects of rice cleaning and cooking process on the residues of flutolanil, fenobucarb, silafluofen and buprofezin in rice].
Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi 44(1) , 7-12, (2003) We studied the effect of cleaning and cooking on the residues of flutolanil, fenobucarb, silafluofen and buprofezin in rice. The rice had been sprayed in a paddy field in Wakayama city, with 3 kinds of pesticide application protocols: spraying once at the usu... |
|
|
Buprofezin inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity in B-biotype Bemisia tabaci.
J. Mol. Neurosci. 30(1-2) , 39-40, (2006) B-biotype Bemisia tabaci is a severe insect pest worldwide in many ornamental, agricultural, and horticultural industries. Control of this insect is hampered by resistance to many acetylcholinesterase (AChE)-inhibiting insecticides, such as organophosphates a... |