D-(-)-Quinic acid
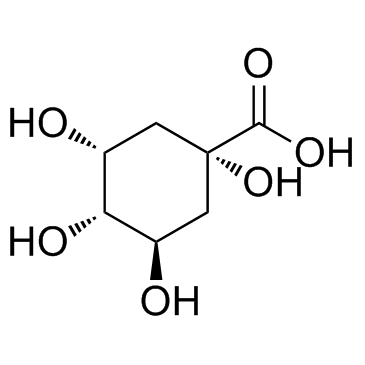
D-(-)-Quinic acid structure
|
Common Name | D-(-)-Quinic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 77-95-2 | Molecular Weight | 192.167 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 438.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H12O6 | Melting Point | 165-170 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 233.1±25.2 °C | |
|
Antioxidant properties, phenolic composition and potentiometric sensor array evaluation of commercial and new blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) and bog blueberry (Vaccinium uliginosum) genotypes.
Food Chem. 188 , 583-90, (2015) Antioxidant properties of juices of newly bred and known blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) genotypes and wild bog blueberry (Vaccinium uliginosum) were evaluated by ABTS(+) scavenging capacity (RSC), ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), oxygen radical abs... |
|
|
Investigating the potential of under-utilised plants from the Asteraceae family as a source of natural antimicrobial and antioxidant extracts.
Food Chem. 161 , 79-86, (2014) Antimicrobial properties of ethanol and water extracts from eight Asteraceae species were investigated against three Gram positive (Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and Bacillus cereus) and two Gram negative (Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium) bacterial ... |
|
|
Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression.
Nature 457(7231) , 910-4, (2009) Multiple, complex molecular events characterize cancer development and progression. Deciphering the molecular networks that distinguish organ-confined disease from metastatic disease may lead to the identification of critical biomarkers for cancer invasion an... |
|
|
Developmental changes in leaf phenolics composition from three artichoke cvs. (Cynara scolymus) as determined via UHPLC-MS and chemometrics.
Phytochemistry 108 , 67-76, (2014) The metabolomic differences in phenolics from leaves derived from 3 artichoke cultivars (Cynara scolymus): American Green Globe, French Hyrious and Egyptian Baladi, collected at different developmental stages, were assessed using UHPLC-MS coupled to chemometr... |
|
|
Differentiation of degrees of ripeness of Catuai and Tipica green coffee by chromatographical and statistical techniques.
Food Chem. 174 , 637-42, (2014) The quality of green coffee is influenced by the degree of ripeness of the fruit at harvest. The aim of this study was to identify chemical markers differentiating between degrees of ripeness. Two coffee varieties, Catuai and Tipica, from the same farm were a... |
|
|
Application of gas chromatography/flame ionization detector-based metabolite fingerprinting for authentication of Asian palm civet coffee (Kopi Luwak).
J. Biosci. Bioeng. 120 , 555-61, (2015) Development of authenticity screening for Asian palm civet coffee, the world-renowned priciest coffee, was previously reported using metabolite profiling through gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS). However, a major drawback of this approach is the h... |
|
|
High gastrointestinal permeability and local metabolism of naringenin: influence of antibiotic treatment on absorption and metabolism.
Br. J. Nutr. 114 , 169-80, (2015) The present study aims to determine the permeability of naringenin in the stomach, small intestine and colon, to evaluate intestinal and hepatic first-pass metabolism, and to study the influence of the microbiota on the absorption and disposition of naringeni... |
|
|
Physico-chemical properties, antioxidant activity and mineral contents of pineapple genotypes grown in china.
Molecules 19(6) , 8518-32, (2014) The fruit physico-chemical properties, antioxidant activity and mineral contents of 26 pineapple [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] genotypes grown in China were measured. The results showed great quantitative differences in the composition of these pineapple genoty... |
|
|
Efficient ethanol production from brown macroalgae sugars by a synthetic yeast platform.
Nature 505(7482) , 239-43, (2014) The increasing demands placed on natural resources for fuel and food production require that we explore the use of efficient, sustainable feedstocks such as brown macroalgae. The full potential of brown macroalgae as feedstocks for commercial-scale fuel ethan... |
|
|
UHPLC-PDA-ESI-TOF/MS metabolic profiling of Arctostaphylos pungens and Arctostaphylos uva-ursi. A comparative study of phenolic compounds from leaf methanolic extracts.
Phytochemistry 115 , 79-88, (2015) The aim of this study was to get a rapid metabolic fingerprinting and to gain insight into the metabolic profiling of Arctostaphylos pungens H. B. K., a plant morphologically similar to Arctostaphylos uva-ursi (L.) Spreng. (bearberry) but with a lower arbutin... |