Glycol sulfite
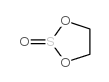
Glycol sulfite structure
|
Common Name | Glycol sulfite | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3741-38-6 | Molecular Weight | 108.11600 | |
| Density | 1.426 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 159.1 °C(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H4O3S | Melting Point | -17ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 175 °F | |
|
Sensing of triacylglycerol in the gut: different mechanisms for fatty acids and 2-monoacylglycerol.
J. Physiol. 593(8) , 2097-109, (2015) Sensing of dietary triacylglycerol in the proximal small intestine results in physiological, hormonal and behavioural responses. However, the exact physiological pathways linking intestinal fat sensing to food intake and the activation of brain circuits remai... |
|
|
Mechanism of chemical degradation and determination of solubility by kinetic modeling of the highly unstable sesquiterpene lactone nobilin in different media.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(10) , 3139-52, (2014) The objective of this work was first to investigate the chemical degradation of the sesquiterpene lactone nobilin and determine its solubility under conditions of concurrent degradation for partially amorphous starting material; second, to determine the effec... |
|
|
Predicting the oral pharmacokinetic profiles of multiple-unit (pellet) dosage forms using a modeling and simulation approach coupled with biorelevant dissolution testing: case example diclofenac sodium.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 87(2) , 236-43, (2014) The objective of this research was to characterize the dissolution profile of a poorly soluble drug, diclofenac, from a commercially available multiple-unit enteric coated dosage form, Diclo-Puren® capsules, and to develop a predictive model for its oral phar... |
|
|
Non-linear increases in danazol exposure with dose in older vs. younger beagle dogs: the potential role of differences in bile salt concentration, thermodynamic activity, and formulation digestion.
Pharm. Res. 31(6) , 1536-52, (2014) To explore the possibility that age-related changes in physiology may result in differences in drug bioavailability after oral administration of lipid based formulations of danazol.Danazol absorption from lipid formulations with increasing drug load was exami... |
|
|
An in vitro digestion test that reflects rat intestinal conditions to probe the importance of formulation digestion vs first pass metabolism in Danazol bioavailability from lipid based formulations.
Mol. Pharm. 11(11) , 4069-83, (2014) The impact of gastrointestinal (GI) processing and first pass metabolism on danazol oral bioavailability (BA) was evaluated after administration of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) in the rat. Danazol absolute BA was determined following oral an... |
|
|
Toward the establishment of standardized in vitro tests for lipid-based formulations, part 4: proposing a new lipid formulation performance classification system.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(8) , 2441-55, (2014) The Lipid Formulation Classification System Consortium looks to develop standardized in vitro tests and to generate much-needed performance criteria for lipid-based formulations (LBFs). This article highlights the value of performing a second, more stressful ... |
|
|
'Stealth' lipid-based formulations: poly(ethylene glycol)-mediated digestion inhibition improves oral bioavailability of a model poorly water soluble drug.
J. Control. Release 192 , 219-27, (2014) For over 20years, stealth drug delivery has been synonymous with nanoparticulate formulations and intravenous dosing. The putative determinants of stealth in these applications are the molecular weight and packing density of a hydrophilic polymer (commonly po... |
|
|
Lipidic dispersion to reduce food dependent oral bioavailability of fenofibrate: In vitro, in vivo and in silico assessments.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 96 , 207-16, (2015) Novel formulations that overcome the solubility limitations of poorly water soluble drugs (PWSD) are becoming ever more critical to a drug development process inundated with these compounds. There is a clear need for developing bio-enabling formulation approa... |
|
|
Lipid-based formulations solidified via adsorption onto the mesoporous carrier Neusilin® US2: effect of drug type and formulation composition on in vitro pharmaceutical performance.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(6) , 1734-46, (2014) The current study determined the extent to which the desorption of lipid-based formulations (LBFs) from a mesoporous magnesium aluminometasilicate (Neusilin®-US2) carrier is governed by drug properties, LBF composition, and LBF-to-adsorbent ratio. A secondary... |
|
|
Development of novel docetaxel phospholipid nanoparticles for intravenous administration: quality by design approach.
AAPS PharmSciTech 16 , 855-64, (2015) The objective of this study was to develop novel docetaxel phospholipid nanoparticles (NDPNs) for intravenous administration. Modified solvent diffusion-evaporation method was adopted in the NDPN preparation. Central composite design (CCD) was employed in the... |