N-Ethylformamide
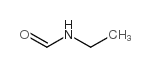
N-Ethylformamide structure
|
Common Name | N-Ethylformamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 627-45-2 | Molecular Weight | 73.09380 | |
| Density | 0.950 g/mL at 20ºC(lit.) | Boiling Point | 202-204ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO | Melting Point | -60.43°C (estimate) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 67ºC | |
|
N-methylformamide: antitumour activity and metabolism in mice.
Br. J. Cancer 45(6) , 843-50, (1982) The antitumour activities of N-methylformamide, N-ethylformamide and formamide against a number of murine tumours in vivo (Sarcoma 180, M5076 ovarian sarcoma and TLX5 lymphoma) have been estimated. In all cases N-methyl-formamide had significant activity, for... |
|
|
Cloning and expression of rat CYP2E1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: detection of genotoxicity of N-alkylformamides.
Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 36(2) , 97-104, (2000) A cDNA coding for rat cytochrome P450 2E1 was cloned into the multicopy vector pYeDP60 and expressed in haploid RSY6 and diploid RS112 yeast strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under control of the GAL10-CYC1 promoter. Spectral and catalytic properties of the... |
|
|
An investigation of the relationship between the hepatotoxicity and the metabolism of N-alkylformamides.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 240(1) , 265-70, (1987) The hepatotoxicity and metabolism of the following close analogs of the hepatotoxic antitumor agent N-methylformamide (NMF) were investigated in CBA/CA mice: N-ethylformamide (NEF), dimethylformamide (DMF), formamide and N-methylacetamide (NMA). Apart from NM... |
|
|
N-alkylformamides are metabolized to N-alkylcarbamoylating species by hepatic microsomes from rodents and humans.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 3(4) , 357-62, (1990) Hepatotoxic formamides such as N-methylformamide (NMF) and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) are metabolized in vivo to N-acetyl-S-(N-methylcarbamoyl)cysteine via oxidation at the formyl carbon, which yields a reactive intermediate. The hypothesis was tested that t... |
|
|
Characterization of the yeast DGK1-encoded CTP-dependent diacylglycerol kinase.
J. Biol. Chem. 283(29) , 20443-53, (2008) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae DGK1 gene encodes a diacylglycerol kinase enzyme that catalyzes the formation of phosphatidate from diacylglycerol. Unlike the diacylglycerol kinases from bacteria, plants, and animals, the yeast enzyme utilizes CTP, instead of AT... |
|
|
Alkylformamides as inducers of tumour cell differentiation--a mini-review.
Toxicology 43(3) , 239-49, (1987) The induction of terminal differentiation in tumour cells represents a possible therapeutic strategy for treating cancer. The alkylformamides are 1 group of experimental compounds which have been shown to induce terminal differentiation in human HL-60 leukemi... |