P-NITROPHENYLACETATE
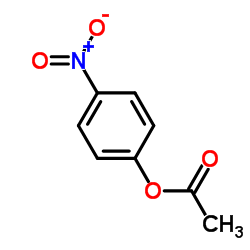
P-NITROPHENYLACETATE structure
|
Common Name | P-NITROPHENYLACETATE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 830-03-5 | Molecular Weight | 181.145 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 296.8±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7NO4 | Melting Point | 75-77 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 145.2±24.6 °C | |
|
Purification and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus bacillithiol transferase BstA.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840(9) , 2851-61, (2014) Gram-positive bacteria in the phylum Firmicutes synthesize the low molecular weight thiol bacillithiol rather than glutathione or mycothiol. The bacillithiol transferase YfiT from Bacillus subtilis was identified as a new member of the recently discovered Din... |
|
|
Production of medium-chain volatile flavour esters in Pichia pastoris whole-cell biocatalysts with extracellular expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae acyl-CoA:ethanol O-acyltransferase Eht1 or Eeb1.
Springerplus 4 , 467, (2015) Medium-chain volatile flavour esters are important molecules since they have extensive applications in food, fragrance, cosmetic, paint and coating industries, which determine different characteristics of aroma or taste in commercial products. Biosynthesis of... |
|
|
One-pot enzymatic conversion of carbon dioxide and utilization for improved microbial growth.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 49(7) , 4466-72, (2015) We developed a process for one-pot CO2 conversion and utilization based on simple conversion of CO2 to bicarbonate at ambient temperature with no energy input, by using the cross-linking-based composites of carboxylated polyaniline nanofibers (cPANFs) and car... |
|
|
Legionella dumoffii utilizes exogenous choline for phosphatidylcholine synthesis.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15(5) , 8256-79, (2014) Phosphatidycholine (PC) is the major membrane-forming phospholipid in eukaryotes but it has been found in only a limited number of prokaryotes. Bacteria synthesize PC via the phospholipid N-methylation pathway (Pmt) or via the phosphatidylcholine synthase pat... |
|
|
Medium-based optimization of an organic solvent-tolerant extracellular lipase from the isolated halophilic Alkalibacillus salilacus.
Extremophiles 19 , 933-47, (2015) A haloalkaliphilic solvent-tolerant lipase was produced from Alkalibacillus salilacus within 48 h of growth in liquid medium. An overall 4.9-fold enhanced production was achieved over unoptimized media after medium optimization by statistical approaches. Plac... |
|
|
Directed evolution of new and improved enzyme functions using an evolutionary intermediate and multidirectional search.
ACS Chem. Biol. 10(2) , 611-21, (2015) The ease with which enzymes can be adapted from their native roles and engineered to function specifically for industrial or commercial applications is crucial to enabling enzyme technology to advance beyond its current state. Directed evolution is a powerful... |
|
|
Antimicrobial properties and mechanism of volatile isoamyl acetate, a main flavour component of Japanese sake (Ginjo-shu).
J. Appl. Microbiol. , doi:10.1111/jam.12764, (2015) To evaluate the antimicrobial properties of the main Ginjo-flavour components of sake, volatile isoamyl acetate and isoamyl alcohol.Volatile isoamyl acetate and isoamyl alcohol both inhibited growth of the five yeast and 10 bacterial test strains. The minimum... |
|
|
Human Coronavirus HKU1 Spike Protein Uses O-Acetylated Sialic Acid as an Attachment Receptor Determinant and Employs Hemagglutinin-Esterase Protein as a Receptor-Destroying Enzyme.
J. Virol. 89 , 7202-13, (2015) Human coronavirus (hCoV) HKU1 is one of six hCoVs identified to date and the only one with an unidentified cellular receptor. hCoV-HKU1 encodes a hemagglutinin-esterase (HE) protein that is unique to the group a betacoronaviruses (group 2a). The function of H... |
|
|
Evidence of multiple/cross resistance to Bt and organophosphate insecticides in Puerto Rico population of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda.
Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 122 , 15-21, (2015) Fall armyworm (FAW) is a damaging pest of many economic crops. Long-term use of chemical control prompted resistance development to many insecticide classes. Many populations were found to be significantly less susceptible to major Bt toxins expressed in tran... |
|
|
Anti-diabetic and spasmolytic potential of Farsetia hamiltonii Royle from Cholistan desert.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 156 , 347-52, (2014) Folk herbal practitioners of the Cholistan desert claim Farsetia hamiltonii Royle (Brassicaceae) to treat diabetes, oxidative damages, diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps. The aim of this study was to scientifically find the potential of Farsetia hamiltonii... |