DIF-1
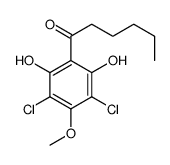
DIF-1 structure
|
Common Name | DIF-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 111050-72-7 | Molecular Weight | 307.17000 | |
| Density | 1.325g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 434.3ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H16Cl2O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 216.5ºC | |
|
Pharmacological evidence that stalk cell differentiation involves increases in the intracellular Ca(2+) and H(+) concentrations in Dictyostelium discoideum.
Dev. Growth Differ. 49(3) , 253-64, (2007) Differentiation-inducing factors (DIFs) are required for stalk cell formation in Dictyostelium discoideum. In the present study, in order to support our hypothesis that DIFs may function via increases in [Ca(2+)](c) and [H(+)](c), we investigated the combined... |
|
|
A specific pathway inducing autophagic cell death is marked by an IP3R mutation.
Autophagy 4(3) , 349-50, (2008) Three main advantages make Dictyostelium a very favorable model to study the induction of autophagic cell death in vitro. First, its small, sequenced and haploid genome facilitates genetic approaches. Second, the Dictyostelium genome does not encode the two m... |
|
|
Autophagic or necrotic cell death in the absence of caspase and bcl-2 family members.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 363(3) , 536-41, (2007) How is one to investigate autophagic or necrotic cell death in the absence of interference from the apoptosis machinery? In the protist Dictyostelium, a model for the study of these two cell death types, we previously showed that autophagic cell death does no... |
|
|
Differentiation-inducing factor-1 enhances 5-fluorouracil action on oral cancer cells inhibiting E2F1 and thymidylate synthase mRNAs accumulation.
Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 69(4) , 983-9, (2012) Differentiation-inducing factor-1 (DIF-1) is a morphogen originally identified in the amoebozoan Dictyostelium discoideum. In mammalian cells, it has been shown to activate GSK3β, which in turn is expected to reduce levels of β-catenin and cyclin D1, thus med... |
|
|
DIF-1 regulates Dictyostelium basal disc differentiation by inducing the nuclear accumulation of a bZIP transcription factor
Dev. Biol. 354(1) , 77-86, (2011) Exposure of monolayer Dictyostelium cells to the signalling polyketide DIF-1 causes DimB, a bZIPtranscription factor, to accumulate in the nucleus where it induces prestalk gene expression. Here we analyse DimB signalling during normal development. In slugs D... |
|
|
[Anti-tumor effects of stalk-differentiation-inducing factor (DIF-1) of Dictyostelium discoideum].
Seikagaku. 69(10) , 1191-5, (1997)
|
|
|
[Pharmacological activities of the dictyostelium differentiation-inducing factor-1 (DIF-1): Cellular slime molds are fascinating lower eukaryotes!].
Seikagaku. 79(2) , 148-51, (2007)
|
|
|
Identification of des-methyl-DIF-1 methyltransferase in Dictyostelium purpureum.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 76(9) , 1672-6, (2012) The signalling molecule 1-(3,5-dichloro-2,6-dihydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl) hexan-1-one (DIF-1) is required for differentiation and pattern formation in Dictyostelium discoideum development. DIF-1 is synthesized by three enzymes, a hybrid polyketide synthase, a fl... |
|
|
A Dictyostelium SH2 adaptor protein required for correct DIF-1 signaling and pattern formation.
Dev. Biol. 353(2) , 290-301, (2011) Dictyostelium is the only non-metazoan with functionally analyzed SH2 domains and studying them can give insights into their evolution and wider potential. LrrB has a novel domain configuration with leucine-rich repeat, 14-3-3 and SH2 protein-protein interact... |
|
|
Perturbations of the actin cytoskeleton activate a Dictyostelium STAT signalling pathway.
Eur. J. Cell Biol. 91(5) , 420-5, (2012) The Dictyostelium transcription factor STATc is tyrosine phosphorylated and accumulates in the nucleus when cells are exposed either to hyper-osmotic stress or to the prestalk-inducing polyketide DIF-1. In the case of stress STAT activation is mediated by reg... |