Decanoyl-coenzyme A
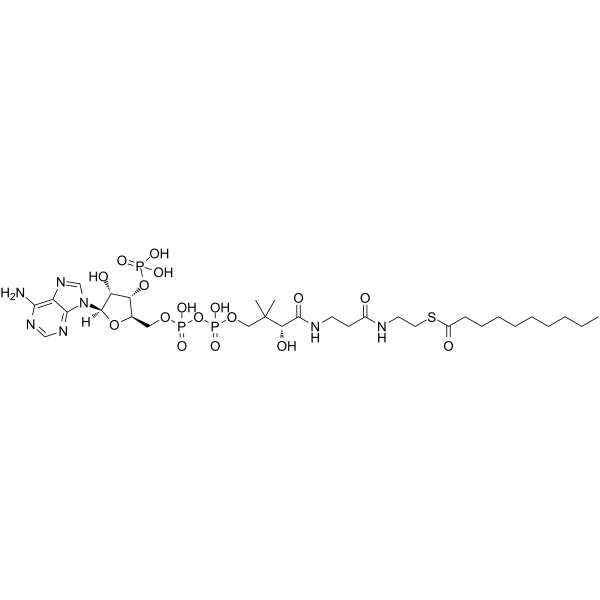
Decanoyl-coenzyme A structure
|
Common Name | Decanoyl-coenzyme A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1264-57-9 | Molecular Weight | 921.78300 | |
| Density | 1.66 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H54N7O17P3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Effect of pH and acyl-CoA chain length on the conversion of heart mitochondrial CPT-I/CPTo to a high affinity, malonyl-CoA-inhibited state.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1290(3) , 261-6, (1996) The effect of pH and acyl-CoA chain length on the conversion of the malonyl-CoA-sensitive carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT-I/CPTo) to a high-affinity, malonyl-CoA-inhibited state using a particle derived from rat heart mitochondria was determined. Preincub... |
|
|
Mechanism of Vibrio cholerae autoinducer-1 biosynthesis.
ACS Chem. Biol. 6 , 356-365, (2011) Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of the disease cholera, uses a cell to cell communication process called quorum sensing to control biofilm formation and virulence factor production. The major V. cholerae quorum-sensing signal CAI-1 has been identified as... |
|
|
Insights into the biosynthesis of the Vibrio cholerae major autoinducer CAI-1 from the crystal structure of the PLP-dependent enzyme CqsA.
J. Mol. Biol. 392 , 763-773, (2009) CqsA is an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of cholerae autoinducer-1 (CAI-1), the major Vibrio cholerae autoinducer engaged in quorum sensing. The amino acid sequence of CqsA suggests that it belongs to the family of alpha-oxoamine synthases that catalyse... |
|
|
Unexpected stereoselective exchange of straight-chain fatty acyl-CoA alpha-protons by human alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase 1A (P504S).
Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 46 , 3348-3350, (2010) Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR; P504S) catalysed exchange of straight-chain fatty acyl-CoA alpha-protons. One alpha-proton was removed in each catalytic cycle, with the pro-S proton preferred. This reaction was most efficient for straight-chain substrat... |
|
|
Acyl coenzyme A esters differentially activate cardiac and beta-cell adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in a side-chain length-specific manner.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 52(10) , 1313-9, (2003) Recent evidence demonstrates that long-chain acyl coenzyme A esters (CoAs) activate cardiac and beta-cell plasma-membrane (pmK(ATP)) adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive potassium channels. In this study, we have investigated the differential effects of acy... |
|
|
Evidence that the medium-chain acyltransferase of lactating-goat mammary-gland fatty acid synthetase is identical with the acetyl/malonyltransferase.
Biochem. J. 227(3) , 981-5, (1985) Competitive binding experiments with malonyl-CoA and [1-14C]acetyl-CoA, [1-14C]butyryl-CoA or [1-14C]decanoyl-CoA indicate that all these substrates are transferred to lactating-goat mammary-gland fatty acid synthetase by the same transferase. Isolation and d... |
|
|
Effect of malonyl-CoA on the kinetics and substrate cooperativity of membrane-bound carnitine palmitoyltransferase of rat heart mitochondria.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 916(3) , 482-92, (1987) The effect of malonyl-CoA on the kinetic parameters of carnitine palmitoyltransferase (outer) the outer form of carnitine palmitoyltransferase (palmitoyl-CoA: L-carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase, EC 2.3.1.21) from rat heart mitochondria was investigated using ... |
|
|
Differential effects of fatty acyl coenzyme A derivatives on citrate synthase and glutamate dehydrogenase.
Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 82(3) , 331-8, (1993) We investigated the hypothesis that one mechanism underlying fatty acid toxicity is the selective inhibition of rate-limiting and/or regulated tricarboxylic acid cycle and related enzymes by fatty acyl coenzyme A (CoA) derivatives by examining the effects of ... |
|
|
Inhibition by etomoxir of rat liver carnitine octanoyltransferase is produced through the co-ordinate interaction with two histidine residues.
Biochem. J. 351 Pt 2 , 495-502, (2000) Rat peroxisomal carnitine octanoyltransferase (COT), which facilitates the transport of medium-chain fatty acids through the peroxisomal membrane, is irreversibly inhibited by the hypoglycaemia-inducing drug etomoxir. To identify the molecular basis of this i... |
|
|
Evidence for a peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation involving D-3-hydroxyacyl-CoAs. Characterization of two forms of hydro-lyase that convert D-(-)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA into 2-trans-enoyl-CoA.
Eur. J. Biochem. 200(1) , 171-8, (1991) A novel D-(-)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA hydro-lyase, forming 2-trans-enoyl-CoA and formerly designated as epimerase (EC 5.1.2.3), was extracted from fat-degrading cotyledons of cucumber seedlings. The enzyme, called D-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA hydro-lyase or D-specific 2-tra... |