N-(3-Fluoranthyl)maleimide
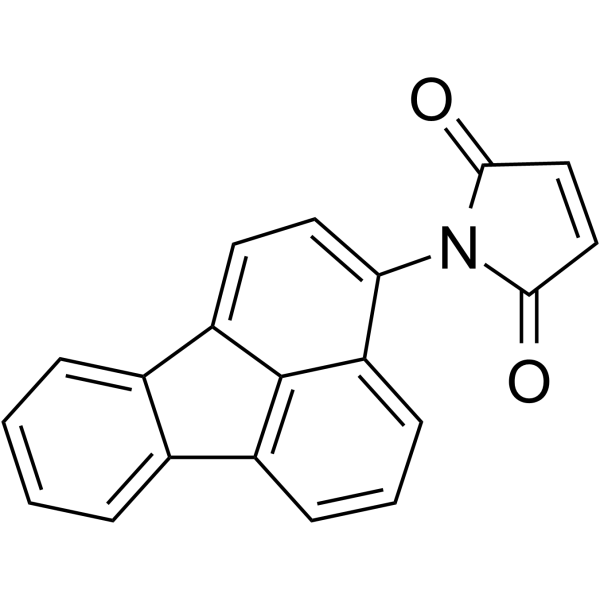
N-(3-Fluoranthyl)maleimide structure
|
Common Name | N-(3-Fluoranthyl)maleimide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 60354-76-9 | Molecular Weight | 297.30700 | |
| Density | 1.466g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 526.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H11NO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 256.1ºC | |
|
Inhibitors of CLK protein kinases suppress cell growth and induce apoptosis by modulating pre-mRNA splicing.
PLoS ONE 10(1) , e0116929, (2015) Accumulating evidence has demonstrated the importance of alternative splicing in various physiological processes, including the development of different diseases. CDC-like kinases (CLKs) and serine-arginine protein kinases (SRPKs) are components of the splici... |
|
|
Large-scaled metabolic profiling of human dermal fibroblasts derived from pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients and healthy controls.
PLoS ONE 9(9) , e108336, (2014) Mutations in the ABC transporter ABCC6 were recently identified as cause of Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), a rare genetic disorder characterized by progressive mineralization of elastic fibers. We used an untargeted metabolic approach to identify biochemical... |
|
|
Disrupting SUMOylation enhances transcriptional function and ameliorates polyglutamine androgen receptor-mediated disease.
J. Clin. Invest. 125(2) , 831-45, (2015) Expansion of the polyglutamine (polyQ) tract within the androgen receptor (AR) causes neuromuscular degeneration in individuals with spinobulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA). PolyQ AR has diminished transcriptional function and exhibits ligand-dependent proteotoxi... |
|
|
Nuclear localization of SMN and FUS is not altered in fibroblasts from patients with sporadic ALS.
Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal Degener. 15(7-8) , 581-7, (2014) Abstract Sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease with no established biological marker. Recent observation of a reduced number of gems (survival motor neuron protein (SMN)-positive nuclear bodies) in cells from patien... |
|
|
Nicotinamide exacerbates hypoxemia in ventilator-induced lung injury independent of neutrophil infiltration.
PLoS ONE 10(4) , e0123460, (2015) Ventilator-induced lung injury is a form of acute lung injury that develops in critically ill patients on mechanical ventilation and has a high degree of mortality. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that is highly upregulated in ventilator-i... |
|
|
Ciliary abnormalities in senescent human fibroblasts impair proliferative capacity.
Cell Cycle 13(17) , 2773-9, (2014) Somatic cells senesce in culture after a finite number of divisions indefinitely arresting their proliferation. DNA damage and senescence increase the cellular number of centrosomes, the 2 microtubule organizing centers that ensure bipolar mitotic spindles. C... |
|
|
Nitric oxide donors increase PVR/CD155 DNAM-1 ligand expression in multiple myeloma cells: role of DNA damage response activation.
BMC Cancer 15 , 17, (2015) DNAX accessory molecule-1 (DNAM-1) is an activating receptor constitutively expressed by macrophages/dendritic cells and by T lymphocytes and Natural Killer (NK) cells, having an important role in anticancer responses; in this regard, combination therapies ab... |
|
|
Sulfation modulates the cell uptake, antiradical activity and biological effects of flavonoids in vitro: An examination of quercetin, isoquercitrin and taxifolin.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 23 , 5402-9, (2015) Quercetin 3'-O-sulfate is one of the main metabolites of the natural flavonoid quercetin in humans. This study was designed to prepare quercetin 3'-O-sulfate (1), isoquercitrin 4'-O-sulfate (2) and taxifolin 4'-O-sulfate (3) by the sulfation of quercetin, iso... |
|
|
PTEN mediates Notch-dependent stalk cell arrest in angiogenesis.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7935, (2015) Coordinated activity of VEGF and Notch signals guides the endothelial cell (EC) specification into tip and stalk cells during angiogenesis. Notch activation in stalk cells leads to proliferation arrest via an unknown mechanism. By using gain- and loss-of-func... |
|
|
BAFF activation of the ERK5 MAP kinase pathway regulates B cell survival.
J. Exp. Med. 212 , 883-92, (2015) B cell activating factor (BAFF) stimulation of the BAFF receptor (BAFF-R) is essential for the homeostatic survival of mature B cells. Earlier in vitro experiments with inhibitors that block MEK 1 and 2 suggested that activation of ERK 1 and 2 MAP kinases is ... |