Galβ(1-3)GalNAc
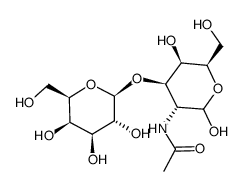
Galβ(1-3)GalNAc structure
|
Common Name | Galβ(1-3)GalNAc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 20972-29-6 | Molecular Weight | 383.34800 | |
| Density | 1.64 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 795.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H25NO11 | Melting Point | 159-160ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 434.9ºC | |
|
Sp1 sites in the noncoding control region of BK polyomavirus are key regulators of bidirectional viral early and late gene expression.
J. Virol. 89(6) , 3396-411, (2015) In kidney transplant patients with BK polyomavirus (BKPyV) nephropathy, viral variants arise bearing rearranged noncoding control regions (rr-NCCRs) that increase viral early gene expression, replicative fitness, and cytopathology. rr-NCCRs result from variou... |
|
|
Chromosome Missegregation Associated with RUVBL1 Deficiency.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0133576, (2015) RUVBL1 (RuvB-like1) and RUVBL2 (RuvB-like 2) are integral components of multisubunit protein complexes involved in processes ranging from cellular metabolism, transcription and chromatin remodeling to DNA repair. Here, we show that although RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 ... |
|
|
Loss of PHD3 allows tumours to overcome hypoxic growth inhibition and sustain proliferation through EGFR.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5582, (2014) Solid tumours are exposed to microenvironmental factors such as hypoxia that normally inhibit cell growth. However, tumour cells are capable of counteracting these signals through mechanisms that are largely unknown. Here we show that the prolyl hydroxylase P... |
|
|
Thrombospondin-1 repression is mediated via distinct mechanisms in fibroblasts and epithelial cells.
Oncogene 34 , 2823-35, (2015) Tumor-associated angiogenesis is postulated to be regulated by the balance between pro- and anti-angiogenic factors. We demonstrate here that the critical step in establishing the angiogenic capability of human tumor cells is the repression of a key secreted ... |
|
|
Polyomavirus T antigens activate an antiviral state.
Virology 476 , 377-85, (2015) Ectopic expression of Simian Virus 40 (SV40) large T antigen (LT) in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) increased levels of mRNAs encoding interferon stimulated genes (ISGs). The mechanism by which T antigen increases levels of ISGs in MEFs remains unclear. W... |
|
|
NGX6a is degraded through a proteasome-dependent pathway without ubiquitination mediated by ezrin, a cytoskeleton-membrane linker.
J. Biol. Chem. 289(52) , 35731-42, (2014) Our previous study demonstrated that the NGX6b gene acts as a suppressor in the invasion and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Recently, we identified the novel isoform NGX6a, which is longer than NGX6b. In this study, we first found that NGX6a was... |
|
|
JMJD1A is a signal-sensing scaffold that regulates acute chromatin dynamics via SWI/SNF association for thermogenesis.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7052, (2015) Histone 3 lysine 9 (H3K9) demethylase JMJD1A regulates β-adrenergic-induced systemic metabolism and body weight control. Here we show that JMJD1A is phosphorylated at S265 by protein kinase A (PKA), and this is pivotal to activate the β1-adrenergic receptor g... |
|
|
UCP-3 uncoupling protein confers hypoxia resistance to renal epithelial cells and is upregulated in renal cell carcinoma.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13450, (2015) Tumor cells can adapt to a hostile environment with reduced oxygen supply. The present study aimed to identify mechanisms that confer hypoxia resistance. Partially hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-resistant proximal tubular (PT) cells were selected by exposing PT ... |
|
|
Cell cycle control and DNA damage response of conditionally immortalized urothelial cells.
PLoS ONE 6(1) , e16595, (2011) Children with complex urogenital anomalies often require bladder reconstruction. Gastrointestinal tissues used in bladder augmentations exhibit a greatly increased risk of malignancy, and the bladder microenvironment may play a role in this carcinogenesis. In... |
|
|
Reversibly Immortalized Mouse Articular Chondrocytes Acquire Long-Term Proliferative Capability While Retaining Chondrogenic Phenotype.
Cell. Transplant. 24 , 1053-66, (2015) Cartilage tissue engineering holds great promise for treating cartilaginous pathologies including degenerative disorders and traumatic injuries. Effective cartilage regeneration requires an optimal combination of biomaterial scaffolds, chondrogenic seed cells... |