(-)-Epicatechin gallate
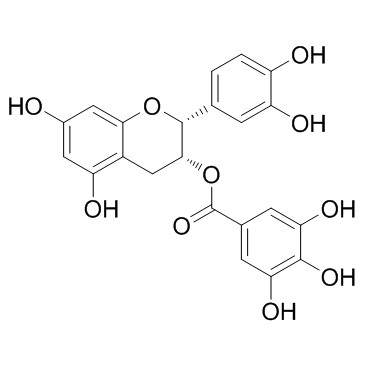
(-)-Epicatechin gallate structure
|
Common Name | (-)-Epicatechin gallate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1257-08-5 | Molecular Weight | 442.372 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 861.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H18O10 | Melting Point | 257-258ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 305.0±27.8 °C | |
|
Influence of different withering conditions on phenolic composition of Avanà, Chatus and Nebbiolo grapes for the production of 'Reinforced' wines.
Food Chem. 194 , 247-56, (2015) The impact of postharvest withering rates on the phenolic composition of 'reinforced' wines produced with partially dehydrated grapes was evaluated. The study was performed on winegrape varieties with anthocyanin profiles differently constituted of di- and tr... |
|
|
Effects of UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic composition of leaves and berries of Vitis vinifera cv. Graciano.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(2) , 409-16, (2014) Ultraviolet (UV) radiation induces adaptive responses that can be used for plant production improvement. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of solar UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic compounds of leaves and berry skins of Vitis vinifera ... |
|
|
Identification of Vitis vinifera L. grape berry skin color mutants and polyphenolic profile.
Food Chem. 194 , 117-27, (2015) A germplasm set of twenty-five grapevine accessions, forming eleven groups of possible berry skin color mutants, were genotyped with twelve microsatellite loci, being eleven of them identified as true color mutants. The polyphenolic profiling of the confirmed... |
|
|
Investigating the potential of under-utilised plants from the Asteraceae family as a source of natural antimicrobial and antioxidant extracts.
Food Chem. 161 , 79-86, (2014) Antimicrobial properties of ethanol and water extracts from eight Asteraceae species were investigated against three Gram positive (Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and Bacillus cereus) and two Gram negative (Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium) bacterial ... |
|
|
Effect of commercially available green and black tea beverages on drug-metabolizing enzymes and oxidative stress in Wistar rats.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 70 , 120-7, (2014) The effect of commercially available green tea (GT) and black tea (BT) drinks on drug metabolizing enzymes (DME) and oxidative stress in rats was investigated. Male Wistar rats were fed a laboratory chow diet and GT or BT drink for 5 weeks. Control rats recei... |
|
|
Ingredients in fruit juices interact with dasatinib through inhibition of BCRP: a new mechanism of beverage-drug interaction.
J. Pharm. Sci. 104(1) , 266-75, (2014) Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are a group of highly novel and target-specific anticancer drugs. Recently, most TKIs are found to be substrates of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP). However, little information... |
|
|
A colourimetric sensor for the simultaneous determination of oxidative status and antioxidant activity on the same membrane: N,N-dimethyl-p-phenylene diamine (DMPD) on Nafion.
Anal. Chim. Acta 865 , 60-70, (2015) A colourimetric sensor capable of simultaneously measuring oxidative status (OS) in terms of the hazard produced by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant activity (AOA) in regard to ROS-scavenging ability of antioxidant compounds was developed. The co... |
|
|
Astringency is a trigeminal sensation that involves the activation of G protein-coupled signaling by phenolic compounds.
Chem. Senses 39(6) , 471-87, (2014) Astringency is an everyday sensory experience best described as a dry mouthfeel typically elicited by phenol-rich alimentary products like tea and wine. The neural correlates and cellular mechanisms of astringency perception are still not well understood. We ... |
|
|
UHPLC-UV method for the determination of flavonoids in dietary supplements and for evaluation of their antioxidant activities.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 468-75, (2015) A simple and rapid ultra-high performance liquid chromatographic (UHPLC) method coupled with an ultraviolet detector (UV) has been developed and validated for the separation and determination of 14 major flavonoids ((±)-catechin, (-)-epicatechin, glycitin, (-... |
|
|
A galloylated dimeric proanthocyanidin from grape seed exhibits dentin biomodification potential.
Fitoterapia 101 , 169-78, (2015) Grape seeds are a rich source of polyphenols, especially proanthocyanidins (PACs), and are also known for the presence of galloylated oligomeric PACs (OPACs). The present study focuses on the phytochemical methodology for grape seed (O)PACs and their potentia... |