Cholesteryl arachidonate
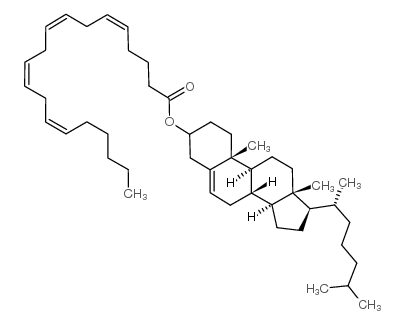
Cholesteryl arachidonate structure
|
Common Name | Cholesteryl arachidonate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 604-34-2 | Molecular Weight | 673.10500 | |
| Density | 0.97g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 697.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C47H76O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 376.9ºC | |
|
Analysis of adrenal cholesteryl esters by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography.
J. Lipid Res. 35(6) , 1115-21, (1994) A reversed phase high performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method was developed for direct profiling and determination of adrenal cholesteryl ester composition. Cholesteryl adrenate and cholesteryl cervonate, which are not commercially available, were sy... |
|
|
Microquantification of cholesterol and cholesteryl esters in rat peritoneal macrophages by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography.
Anal. Biochem. 185(2) , 339-45, (1990) A simple and rapid method for the microquantification of cholesterol and cholesteryl esters by reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography has been established. Comparison of elution patterns of authentic cholesterol and cholesteryl esters revealed t... |
|
|
Flow cytometric measurement of ceroid accumulation in macrophages.
Atherosclerosis 98(2) , 229-39, (1993) Flow cytometry has been examined as a method for quantitative measurement of the accumulation in macrophages of ceroid, an autofluorescent polymer composed of oxidised protein and lipid. Murine peritoneal macrophages were cultured in the presence of cholester... |
|
|
Novel surface phase containing cholesteryl esters. 2. Nonequivalence of cholesteryl arachidonate and those with 18-carbon, cis-unsaturated acyl groups.
Biochemistry 20(4) , 724-30, (1981) Surface pressure--area isotherms for binary mixtures of cholesteryl octanoate, elaidate, stearate, oleate, linoleate, linolenate, and arachiodonate in mixtures with dioleoyllecithin, triolein, oleic acid, and oleoyl alcohol were measured at 24 degrees C. Anal... |
|
|
Sterol and steryl ester regulation of phospholipase A2 from the mosquito parasite Lagenidium giganteum.
Lipids 31(11) , 1179-88, (1996) Lagenidium giganteum, a facultative parasite of mosquito larvae, cannot synthesize sterols, and requires an exogenous source of these lipids in order to enter its reproductive cycle. This parasite grows vegetatively in the absence of sterols, but requires cho... |
|
|
[Serum cholesterol ester level in patients with ischemic heart disease and liver disease].
Kardiologiia 24(10) , 90-3, (1984) The blood serum of coronary and liver patients was shown to display a similar increase in the relative levels of cholesterololeate and a some what less marked elevation in the content of cholesterol esters with saturated fatty acids. The cholesterollinoleate ... |
|
|
Macrophage cholesteryl ester mobilization and atherosclerosis.
Vascul. Pharmacol. 52 , 1-10, (2010) Accumulation of cholesteryl esters (CE) stored as cytoplasmic lipid droplets is the main characteristic of macrophage foam cells that are central to the development of atherosclerotic plaques. Since only unesterified or free cholesterol (FC) can be effluxed f... |
|
|
Cholesteryl ester hydroperoxides are biologically active components of minimally oxidized low density lipoprotein.
J. Biol. Chem. 283 , 10241-10251, (2008) Oxidation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) occurs in vivo and significantly contributes to the development of atherosclerosis. An important mechanism of LDL oxidation in vivo is its modification with 12/15-lipoxygenase (LO). We have developed a model of minim... |
|
|
Replacement of endogenous cholesteryl esters of low density lipoprotein with exogenous cholesteryl linoleate. Reconstitution of a biologically active lipoprotein particle.
J. Biol. Chem. 253 , 4093-101, (1978)
|
|
|
Cholesteryl hydroperoxyoctadecadienoate from oxidized low density lipoprotein inactivates platelet-derived growth factor.
J. Biol. Chem. 273 , 19405-10, (1998) Both oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) have been implicated in the genesis of various inflammatory responses, including atherosclerosis. We demonstrate here a novel interaction between specific oxidized lipids... |