Aurintricarboxylic acid
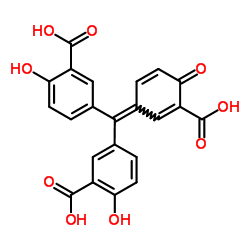
Aurintricarboxylic acid structure
|
Common Name | Aurintricarboxylic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4431-00-9 | Molecular Weight | 422.341 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 759.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H14O9 | Melting Point | 300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 427.1±29.4 °C | |
|
Altered Oligodendrocyte Maturation and Myelin Maintenance: The Role of Antiretrovirals in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders.
J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 74 , 1093-118, (2015) Despite effective viral suppression through combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), approximately half of HIV-positive individuals have HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). Studies of antiretroviral-treated patients have revealed persistent white m... |
|
|
MicroRNA-23a has minimal effect on endurance exercise-induced adaptation of mouse skeletal muscle.
Pflugers Arch. 467(2) , 389-98, (2015) Skeletal muscles contain several subtypes of myofibers that differ in contractile and metabolic properties. Transcriptional control of fiber-type specification and adaptation has been intensively investigated over the past several decades. Recently, microRNA ... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
The adhesive properties of the Staphylococcus lugdunensis multifunctional autolysin AtlL and its role in biofilm formation and internalization.
Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 305(1) , 129-39, (2015) Although it belongs to the group of coagulase-negative staphylococci, Staphylococcus lugdunensis has been known to cause aggressive courses of native and prosthetic valve infective endocarditis with high mortality similar to Staphylococcus aureus. In contrast... |
|
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened seven parasite lines for differences in responses to 1,279... |
|
|
Small molecule inhibitors of Ago2 decrease Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus replication.
Antiviral Res. 112 , 26-37, (2014) Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV) is classified as a Category B Select Agent and potential bioterror weapon for its severe disease course in humans and equines and its potential for aerosol transmission. There are no current FDA licensed vaccines or... |
|
|
Changes in poly(A) tail length dynamics from the loss of the circadian deadenylase Nocturnin.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 17059, (2015) mRNA poly(A) tails are important for mRNA stability and translation, and enzymes that regulate the poly(A) tail length significantly impact protein profiles. There are eleven putative deadenylases in mammals, and it is thought that each targets specific trans... |
|
|
Inhibitory effect of Lactobacillus salivarius on Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation.
Mol. Oral Microbiol. 30(1) , 16-26, (2015) Dental caries arises from an imbalance of metabolic activities in dental biofilms developed primarily by Streptococcus mutans. This study was conducted to isolate potential oral probiotics with antagonistic activities against S. mutans biofilm formation from ... |
|
|
Actinomycin D and nutlin-3a synergistically promote phosphorylation of p53 on serine 46 in cancer cell lines of different origin.
Cell. Signal. 27 , 1677-87, (2015) The p53 tumor suppressor protein is a transcription factor activated by phosphorylation of its N-terminus. MDM2, encoded by a p53-activated gene, acts as a negative-feedback regulator of p53 by promoting p53 degradation. Moreover, MDM2 inhibits p53 by binding... |
|
|
MicroRNA-328 enhances cellular motility through posttranscriptional regulation of PTPRJ in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Onco. Targets Ther. 8 , 3159-67, (2015) Interaction between microRNA (miR-328) and PTPRJ (protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, J) has been reported to be responsible for miR-328-dependent increase in epithelial cancer cell proliferation. However, the role of miR-328 and PTPRJ in hepatocellu... |