2-Heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolinone
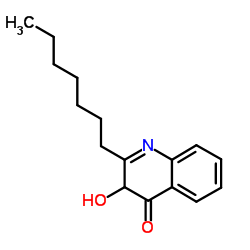
2-Heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolinone structure
|
Common Name | 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolinone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 108985-27-9 | Molecular Weight | 259.343 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 416.8±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H21NO2 | Melting Point | 182-185ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 205.9±28.7 °C | |
|
Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 20th ed., 96 , 11229-11234, (1999) Numerous species of bacteria use an elegant regulatory mechanism known as quorum sensing to control the expression of specific genes in a cell-density dependent manner. In Gram-negative bacteria, quorum sensing systems function through a cell-to-cell signal m... |
|
|
3-indolylacetonitrile decreases Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formation and Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence.
Environ. Microbiol. 13 , 62-73, (2011) Intercellular signal indole and its derivative hydroxyindoles inhibit Escherichia coli biofilm and diminish Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. However, indole and bacterial indole derivatives are unstable in the microbial community because they are quickly deg... |
|
|
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-quinolone signal molecules HHQ and PQS play multifunctional roles in quorum sensing and iron entrapment.
Chem. Biol. 14 , 87-96, (2007) Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone (PQS), a quorum-sensing (QS) signal that regulates numerous virulence genes including those involved in iron scavenging. Biophysical analysis revealed that 2-alkyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolones form ... |
|
|
Differential immune modulatory activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing signal molecules.
Infect. Immun. 72(11) , 6463-6470, (2004) Pseudomonas aeruginosa releases a spectrum of well-regulated virulence factors, controlled by intercellular communication (quorum sensing) and mediated through the production of small diffusible quorum-sensing signal molecules (QSSM). We hypothesize that QSSM... |
|
|
Indole and 7-hydroxyindole diminish Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence.
Microb. Biotechnol. 2 , 75-90, (2009) Indole is an extracellular biofilm signal for Escherichia coli, and many bacterial oxygenases readily convert indole to various oxidized compounds including 7-hydroxyindole (7HI). Here we investigate the impact of indole and 7HI on Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1... |
|
|
7-fluoroindole as an antivirulence compound against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 329 , 36-44, (2012) The emergence of antibiotic resistance has necessitated new therapeutic approaches for combating persistent bacterial infection. An alternative approach is regulation of bacterial virulence instead of growth suppression, which can readily lead to drug resista... |