5-Methylcytidine
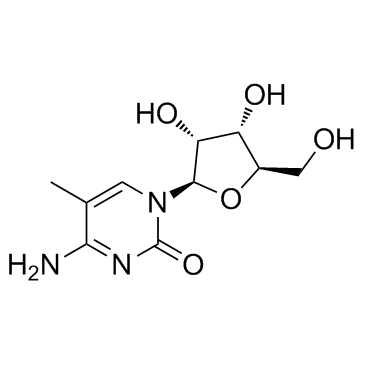
5-Methylcytidine structure
|
Common Name | 5-Methylcytidine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2140-61-6 | Molecular Weight | 257.243 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 537.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H15N3O5 | Melting Point | 212-215 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 278.9±32.9 °C | |
|
Flow-dependent epigenetic DNA methylation regulates endothelial gene expression and atherosclerosis.
J. Clin. Invest. 124(7) , 3187-99, (2014) In atherosclerosis, plaques preferentially develop in arterial regions of disturbed blood flow (d-flow), which alters endothelial gene expression and function. Here, we determined that d-flow regulates genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in a DNA methyltrans... |
|
|
Modulation of the immune system during postpartum uterine inflammation.
Physiol. Genomics 47(4) , 89-101, (2015) Postpartum uterine inflammation (endometritis) in the dairy cow is associated with lower fertility at both the time of infection and after the inflammation has resolved. We hypothesized that aberrant DNA methylation may be involved in the subfertility associa... |
|
|
DNA methylation and differential gene regulation in photoreceptor cell death.
Cell Death Dis. 5 , e1558, (2014) Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) defines a group of inherited degenerative retinal diseases causing progressive loss of photoreceptors. To this day, RP is still untreatable and rational treatment development will require a thorough understanding of the underlying ce... |
|
|
Regulatory network decoded from epigenomes of surface ectoderm-derived cell types.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5442, (2014) Developmental history shapes the epigenome and biological function of differentiated cells. Epigenomic patterns have been broadly attributed to the three embryonic germ layers. Here we investigate how developmental origin influences epigenomes. We compare key... |
|
|
Selective derivatization of cytosine and methylcytosine moieties with 2-bromoacetophenone for submicrogram DNA methylation analysis by reversed phase HPLC with spectrofluorimetric detection.
Anal. Chem. 83(20) , 7999-8005, (2011) In eukaryotes, actual DNA methylation patterns provide biologically important information, for which both, genome-wide and locus-specific methylation at cytosine residues have been extensively studied. The original contribution of this work relies on the sele... |
|
|
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and dimensionality reduction techniques in quantitative structure retention relationship modeling of retention in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1403 , 54-62, (2015) The objective of this study was to model the retention of nucleosides and pterins in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) via QSRR-based approach. Two home-made (Amino-P-C18, Amino-P-C10) and one commercial (IAM.PC.DD2) HILIC stationary phase... |
|
|
Experience-dependent DNA methylation regulates plasticity in the developing visual cortex.
Nat. Neurosci. 18 , 956-8, (2015) DNA methylation is an epigenetic repressor mark for transcription dynamically regulated in neurons. We analyzed visual experience regulation of DNA methylation in mice and its involvement in ocular dominance plasticity of the developing visual cortex. Monocul... |
|
|
The interfering effects of superovulation and vitrification upon some important epigenetic biomarkers in mouse blastocyst.
Cryobiology 69(3) , 419-27, (2014) Appropriate epigenetic changes in preimplantation embryos are critical for embryonic development and successful pregnancy. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of some assisted reproductive techniques (ARTs) on a panel of epigenetic biomarkers by... |
|
|
PEA15 regulates the DNA damage-induced cell cycle checkpoint and oncogene-directed transformation.
Mol. Cell. Biol. , (2014) Regulation of the DNA damage response and cell cycle progression is critical for maintaining genome integrity. Here, we report that in response to DNA damage, COPS5 deubiquitinates and stabilizes PEA15 in an ATM kinase-dependent manner. PEA15 expression oscil... |
|
|
Consistent decrease in global DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation in the hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease patients.
Neurobiol. Aging 34(9) , 2091-9, (2013) Epigenetic dysregulation of gene expression is thought to be critically involved in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Recent studies indicate that DNA methylation and DNA hydroxymethylation are 2 important epigenetic mechanisms that regulate ge... |