3-Hydroxymandelic Acid
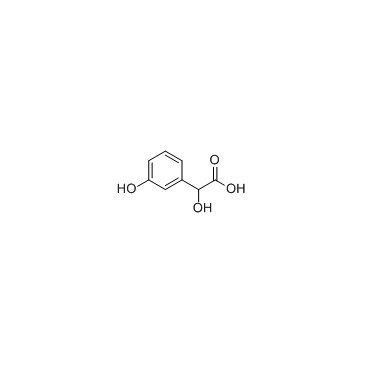
3-Hydroxymandelic Acid structure
|
Common Name | 3-Hydroxymandelic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 17119-15-2 | Molecular Weight | 168.14700 | |
| Density | 1.48g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 424.3ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O4 | Melting Point | 128-132ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 224.5ºC | |
|
Improving the serum D-xylose test for the identification of patients with small intestinal malabsorption.
J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 33(1) , 36-40, (2001) D-Xylose absorption testing is a simple, low-cost method of screening for small intestinal malabsorption. The optimum method to measure D-xylose absorption (serum vs. urine testing) is uncertain.We present a method of improving the accuracy of D-xylose testin... |
|
|
Plasma amino acid profile on nocturnal hemodialysis.
Blood Purif. 18(2) , 97-102, (2000) The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of nocturnal hemodialysis (NHD) on serum amino acid (AA) profile.In a cross-over trial, we studied the AA profile in 11 patients who were switched from conventional hemodialysis to NHD. Plasma levels of AA w... |
|
|
Plasma pteridine concentrations in patients with chronic renal failure.
Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 17(6) , 1032-6, (2002) Pteridine metabolism is impaired in the uraemic state. This may affect cardiovascular function and contribute to malnutrition. We wished to clarify further the impact of impaired pteridine metabolism.Using the HPLC method, the plasma concentrations of endogen... |
|
|
Determination of polyamines in hydrolysates of uremic plasma by high-performance cation-exchange column chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 272(2) , 279-85, (1983) The levels of putrescine, cadaverine, spermidine and spermine in uremic plasma were determined with an automatic polyamine analyzer with a 7.5 X 0.2 cm I.D. cation-exchange column using a stepwise sodium chloride gradient. All four polyamines were higher in t... |
|
|
Circulating tetrahydrobiopterin concentrations in patients with septic shock.
Br. J. Anaesth. 86(4) , 578-80, (2001) Nitric oxide synthase requires tetrahydrobiopterin for its activity. In animal models of sepsis, changes in circulating tetrahydrobiopterin concentrations precede increases in nitrate. We measured plasma tetrahydrobiopterin and nitrate concentrations on three... |
|
|
Serum concentrations of asymmetric (ADMA) and symmetric (SDMA) dimethylarginine in patients with chronic kidney diseases.
Clin. Chim. Acta 336(1-2) , 1-12, (2003) NO synthesis is inhibited by the dimethylarginine (DMA) ADMA, which accumulates, similar to SDMA, in the plasma of patients suffering from chronic renal failure (CRF). ADMA and possibly SDMA contribute to hypertension and atherosclerosis in patients with chro... |
|
|
Statin treatment and diabetes affect myeloperoxidase activity in maintenance hemodialysis patients.
Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1(2) , 281-7, (2006) Myeloperoxidase (MPO), which is secreted during activation of neutrophils, may serve as one mechanistic link among persistent inflammation, oxidative stress, and cardiovascular disease. This study related MPO activity to inflammatory and oxidative stress biom... |
|
|
Oral L-carnitine: metabolite formation and hemodialysis.
Curr. Drug Metab. 7(7) , 811-6, (2006) L-Carnitine has important roles in intermediary metabolism and patients with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing hemodialysis may develop a secondary L-carnitine deficiency. The extent of accumulation of the metabolites trimethylamine and trimethylamin... |
|
|
Plasma free amino acids and their metabolites in Taiwanese patients on hemodialysis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.
Clin. Chim. Acta 364(1-2) , 209-16, (2006) The high prevalence of protein-energy malnutrition is a critical issue for patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD) on hemodialysis (HD) or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). Levels of plasma and intracellular amino acids are significant in... |
|
|
Dimethylglycine accumulates in uremia and predicts elevated plasma homocysteine concentrations.
Kidney Int. 59(6) , 2267-72, (2001) Hyperhomocysteinemia is a risk factor for atherosclerosis that is common in chronic renal failure (CRF), but its cause is unknown. Homocysteine metabolism is linked to betaine-homocysteine methyl transferase (BHMT), a zinc metalloenzyme that converts glycine ... |