β-Glycerol phosphate disodium salt pentahydrate
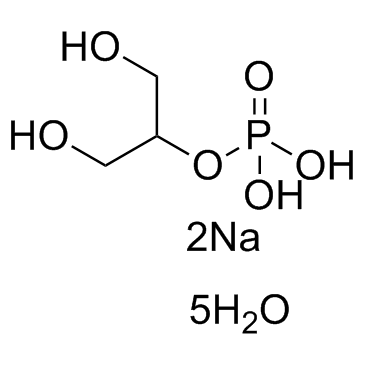
β-Glycerol phosphate disodium salt pentahydrate structure
|
Common Name | β-Glycerol phosphate disodium salt pentahydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13408-09-8 | Molecular Weight | 308.13 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 488.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H19Na2O11P | Melting Point | >300ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 249.1ºC | |
|
P7170, a novel inhibitor of mTORC1/mTORC2 and Activin receptor-like Kinase 1 (ALK1) inhibits the growth of non small cell lung cancer.
Mol. Cancer 13 , 259, (2014) Lung cancer is the major cause of cancer-related deaths and many cases of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), a common type of lung cancer, have frequent genetic/oncogenic activation of EGFR, KRAS, PIK3CA, BRAF, and others that drive tumor growth. Some patien... |
|
|
Polyubiquitin chain-dependent protein degradation in TRIM30 cytoplasmic bodies.
Exp. Mol. Med. 47 , e159, (2015) Viral infection induces numerous tripartite motif (TRIM) proteins to control antiviral immune signaling and viral replication. Particularly, SPRY-containing TRIM proteins are found only in vertebrates and they control target protein degradation by their RING-... |
|
|
Human mesenchymal stem cells as a novel platform for simultaneous evaluation of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of pharmaceuticals.
Mutagenesis 30 , 391-9, (2015) The in vitro micronucleus test is a well-known test for the screening of genotoxic compounds. However until now, most studies have been performed on either human peripheral lymphocytes or established cancer cell lines. This study provides human mesenchymal st... |
|
|
Mesenchymal progenitors aging highlights a miR-196 switch targeting HOXB7 as master regulator of proliferation and osteogenesis.
Stem Cells 33(3) , 939-50, (2015) Human aging is associated with a decrease in tissue functions combined with a decline in stem cells frequency and activity followed by a loss of regenerative capacity. The molecular mechanisms behind this senescence remain largely obscure, precluding targeted... |
|
|
Histone deacetylase inhibition destabilizes the multi-potent state of uncommitted adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.
J. Cell Physiol. 230(1) , 52-62, (2015) Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (AMSCs) grown in platelet lysate are promising agents for therapeutic tissue regeneration. Here, we investigated whether manipulation of epigenetic events by the clinically relevant histone deacetylase inhibitor... |
|
|
Influence of nuclear blebs and micronuclei status on the growth kinetics of human mesenchymal stem cells.
J. Cell Physiol. 230(3) , 657-66, (2014) Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) demands assurance of the quality, safety, and genetic stability. Nuclear blebs (NBs) and Micronuclei (MNs) are considered as biomarkers for cancer and an increase in their numbers is associated with malig... |
|
|
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Heart Rate Variability and Baroreflex Sensitivity in Rats with Chronic Heart Failure.
Stem Cells Dev. 24 , 2181-92, (2015) Heart failure induced by myocardial infarct (MI) attenuates the heart rate variability (HRV) and baroreflex sensitivity, which are important risk factors for life-threatening cardiovascular events. Therapies with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have shown promi... |
|
|
Hdac3 Deficiency Increases Marrow Adiposity and Induces Lipid Storage and Glucocorticoid Metabolism in Osteochondroprogenitor Cells.
J. Bone Miner Res. 31 , 116-28, (2016) Bone loss and increased marrow adiposity are hallmarks of aging skeletons. Conditional deletion of histone deacetylase 3 (Hdac3) in murine osteochondroprogenitor cells causes osteopenia and increases marrow adiposity, even in young animals, but the origins of... |
|
|
The stimulatory effects of eNOS/F92A-Cav1 on NO production and angiogenesis in BMSCs.
Biomed. Pharmacother. 77 , 13-Jul, (2016) Nitric oxide (NO) is generated in endothelial cells by endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). Caveolin-1 (Cav1) inhibits eNOS function and NO production. Modifying Cav1 scaffold domain, in particular Phenylalanine at position 92 (F92) is critical for the i... |
|
|
Microplate-based chromatin immunoprecipitation method, Matrix ChIP: a platform to study signaling of complex genomic events.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36 , e17, (2008) The chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay is a major tool in the study of genomic processes in vivo. This and other methods are revealing that control of gene expression, cell division and DNA repair involves multiple proteins and great number of their m... |